The Intel Core i9 10900K is the most powerful processor that we can find right now within the general consumer catalog of the chip giant. If we compare it with the Intel Core i5 10600K we find the same base at the level of architecture and platform, but we also see important differences.
A performance review of Intel Core i9 10900K
Both processors start from the same base, the Comet Lake-S architecture, which means that they are manufactured in the 14 nm ++ process and have the same IPC. We are facing the same manufacturing process that we have seen in the 9th generation Intel Core, based on the Coffee Lake Refresh architecture, but Intel has introduced important changes in this new architecture that positively affect working temperatures.
Among the most interesting changes is the reduction of the thickness of the silicon, which makes the heat generated has a more limited path, the use of a thinner encapsulation, and the use of solder instead of thermal paste in the IHS. If we put all this together, the conclusion is clear, by having a design based on thinner silicon matrices and welding in the IHS, working temperatures are improved.

Improving the working temperatures in a processor like the Intel Core i5 10600K is not essential, after all, we are facing a 6-core, 12-thread processor, but in the case of the Intel Core i9 10900K things change, and a lot, since we are talking about a “monster” that adds 10 cores and 20 threads with a turbo mode that exceeds 5GHz in frequency, and that on top of it comes with the multiplier unlocked, which means that we can overclock it.
- Intel and UCSC work on a promising alternative to NVIDIA’s DLSS
- Intel targets cheap PCs with Jasper Lake processors
- Tiger Lake: 11th generation Intel Core processors are here
Today the Core i9 10900K has a price of around $540, and we can find the model without an integrated GPU, the Intel Core i9 10900KF, for about $520. If we compare with everything that AMD has right now in that price range we see that its direct rival is the Ryzen 9 3900XT, a chip that has 12 cores and 24 threads running at 3.8GHz-4.7GHz, and that it is you can buy from $530. However, we can also find the Ryzen 9 3900X, which has the same configuration but operates at 3.8GHz-4.6GHz and has a much more attractive price: $460 on average.
As we can see, the high-end is very busy. In terms of price-performance, the Ryzen 9 3900X offers a very solid value, but the Core i9 10900K also offers, as we will see in this review, an interesting value for those who want to achieve the maximum possible performance in games.
Intel Core i9 10900K, a technical look
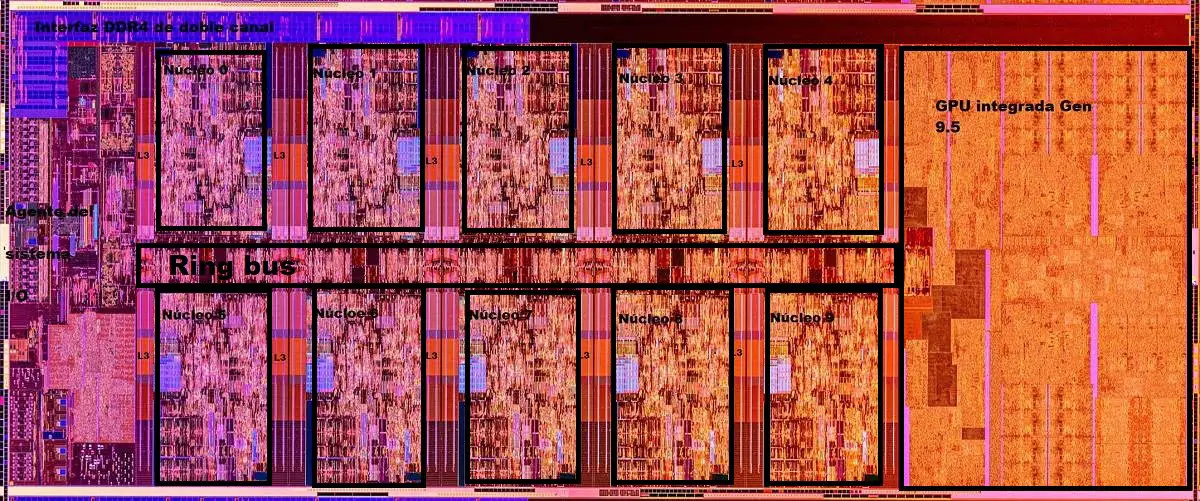
As we said at the beginning of the article the Intel Core i9 10900K uses a monolithic core design, which means that we have a ten-core configuration divided into two rows of five cores. Each core is located next to its corresponding L3 cache block. The distribution of the chip on the silicon tablet is practically identical to that of the Core i5 10600K, the only important difference is found in the addition of two more cores in each row.
If we look at the part on the right we find an integrated Intel Gen 9.5 GPU, a design that has been widely surpassed by the Intel Gen 11 architecture, used by Ice Lake processors (10 nm +). The “northbridge” is on the left, and at the top, we have the 128-bit memory controller (dual channel). The interconnection and communication of all the elements integrated into the silicon chip are carried out by a Ringbus system.
Unlike the Ryzen 9 3900X, which divides its 12 cores into two chiplets of eight cores each, of which only six are active and are interconnected by an Infinity Fabric system, in the Intel Core i9 10900K we have all the cores and the I / O interface integrated into a single silicon chip, with all the advantages that this entails in terms of latencies and caches. This chip adds 20 MB of L3 cache, which is accessible by all cores, while in the AMD chip each chiplet can only access the L3 cache assigned to it.
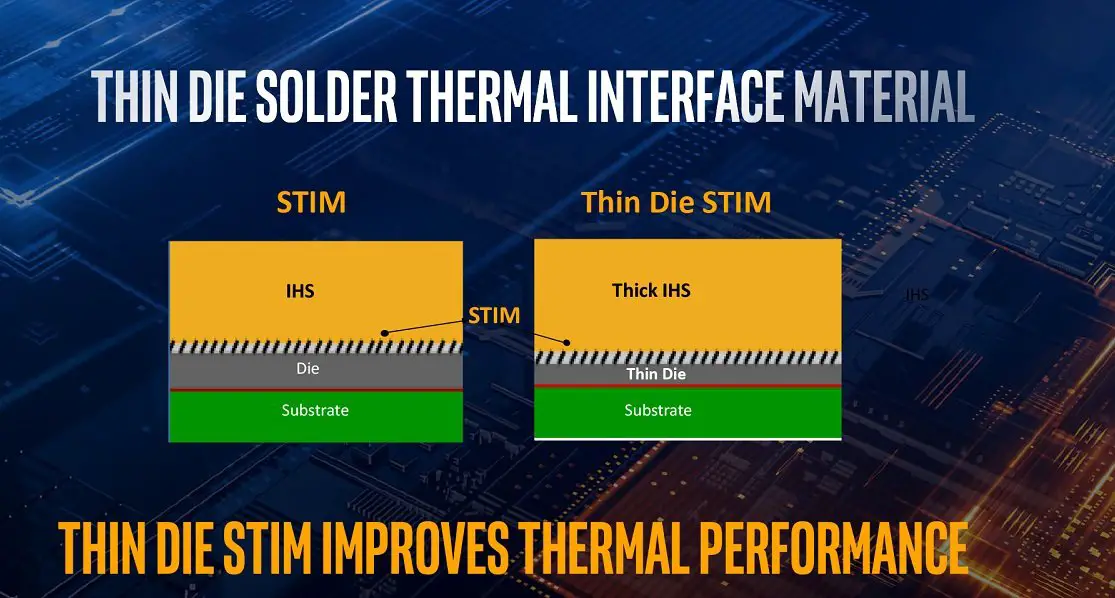
Inside the “northbridge” of the Intel Core i9 10900K, we have a set of important elements, including the complex PCI-E Gen3 as well as the DMI interface and the 128-bit memory controller (dual channel). We have already talked about the GPU and it is not worth delving into it, since it is a model that has been with us for a long time and is not designed to move complex games or demanding applications. All in all, its performance, in general, is not bad if we assess it from a basic point of view, since it moves multimedia content in 4K, supports DisplayPort 1.4 and HDMI 2.0 connectors, and is compatible with HDR10 and Dolby Vision.
- AMD will introduce Zen 3 on October 8, and RDNA 2 on October 28
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080 full specifications
- It’s official: NVIDIA buys ARM for 40 billion dollars
The ten cores that the Intel Core i9 10900K integrates can work with ten processes, and thanks to the inclusion of HyperThreading technology, each core can also work on one thread, which leaves us with that total of 10 cores and 20 threads that we referred to. at first. There is no game today that can effectively take advantage of so many threads, but there are professional applications that can benefit from these types of configurations, and this makes the Intel Core i9 10900K an “all-rounder” chip, capable of offering good performance in both games and professional applications.
It is important to note that although the Intel Core i9 10900K can move 20 threads, this does not mean that it has the same power as a 20-core processor, since the processes are used to carry out more complex tasks, and the threads for tasks less heavy. The Core i9 10900K could simultaneously handle ten heavy tasks and ten lighter tasks, while a 20-core processor could cope with 20 heavy tasks. It is a simple explanation, but effective and easy to understand.

With regard to working frequencies, the Core i9 10900K operates at a base value of 3.7GHz but reaches 5.3GHz with a single active core thanks to the turbo mode. As our regular readers will know, such turbo mode scales dynamically based on workload (takes into account the number of active cores and threads), and is also affected by power and operating temperatures. For this reason, it is essential to accompany the Intel Core i9 10900K with a motherboard that has a good VRM, and a good cooling system.
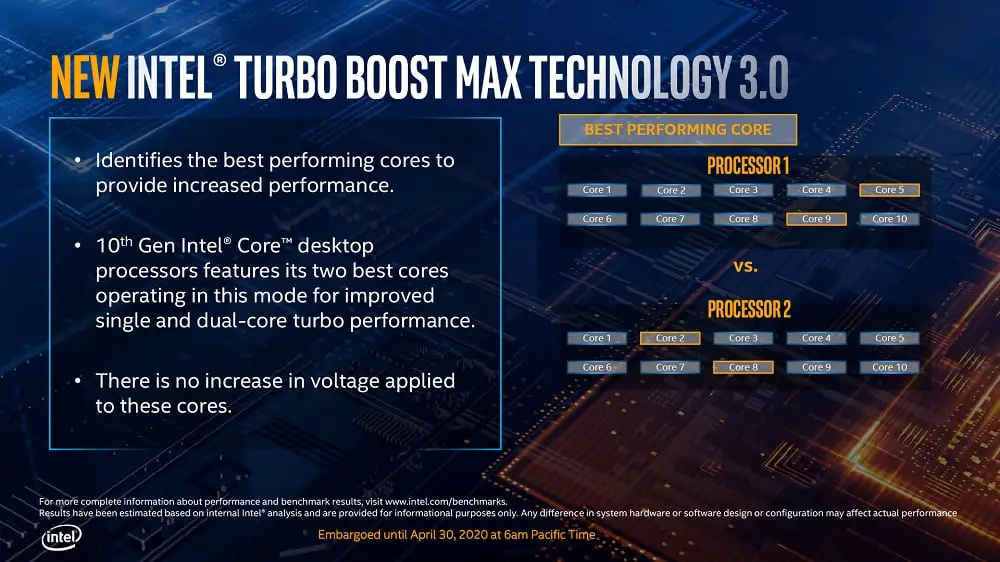
Unlike what we saw in the Intel Core i5 10600K, the Intel Core i9 10900K does use Turbo Boost Max 3.0 and Thermal Velocity Boost technologies, which allows identifying the cores with the best performance and fine-tuning the working speeds according to of the load, of the temperatures and of the feeding. This translates into a very interesting frequency scaling that we break down below:
- Base frequency: 3.7GHz.
- Turbo mode with an active core: up to 5.3GHz in optimal conditions.
- Turbo mode with two cores and two active threads: up to 5.2GHz.
- Turbo mode with two cores and four active threads: 5GHz.
- Turbo mode with all active cores and threads: 4.9GHz.
There is no doubt, the Intel Core i9 10900K has a very aggressive and well-implemented turbo mode that seeks to maximize performance based on each workload. Turbo Boost Max 3.0 and Thermal Velocity Boost technologies play an important role, as the former identifies the two highest-performing cores and takes advantage of them whenever possible, and the latter can add up to 100 MHz in frequency if the temperature is optimal.
We jump now to take a look at the TDP. We find a value of 125 watts, but this being referred to the PL1 value. The important value is the PL2, as it reflects the actual consumption of the processor when the turbo mode comes into operation and is maintained for a sustained period. The Intel Core i9 10900K registers a PL2 value of 250 watts, a high figure that will help you understand why we talk so insistently about the importance of VRM and cooling on motherboards with the Z490 chipset.
The “K” badge indicates that the Intel Core i9 10900K comes with the multiplier unlocked and that we can overclock it without a problem. However, we must bear in mind that the turbo mode is already very tight (4.9GHz with ten cores and twenty active threads is no small feat), which means that we have a fairly low overclocking margin, as we will see later. . that badge also implies that the Intel Core i9 10900K comes without a heatsink.
Intel Core i9 10900K specifications and platform
- Comet Lake-S architecture in 14nm ++ process
- Ten cores and twenty threads at 3.7GHz-5.3GHz, normal, and turbo mode
- Unlocked multiplier (supports overclocking)
- 20MB L3 cache
- 125-watt TDP
- Compatible with LGA 1200 socket and 400 series chipsets
The new Intel Comet Lake-S processors are integrated into a new platform, and therefore need a new motherboard to work, both by chipset and socket. The new generation of Intel is grouped on the different variants of the 400 series chipset and the LGA1200 socket, which means that we cannot mount a Core i9 10900K on a Z390 motherboard.
This strategy by Intel has been widely questioned, especially because motherboards with 400 series chipset and LGA1200 socket lack such important novelties as the support of the PCIE Gen4 standard, but the truth is that they bring notable differences both at the design level. and build quality that affect essential components, such as the VRM and the heatsink system, and that are necessary to meet the demands of such powerful chips like the Intel Core i9 10900K.
- MSI Stealth 15M: MSI’s new gaming laptop
- Crysis Remastered will have ray tracing on Xbox One X and PS4 Pro
- AMD Radeon RX 6800 will have a $549 price tag
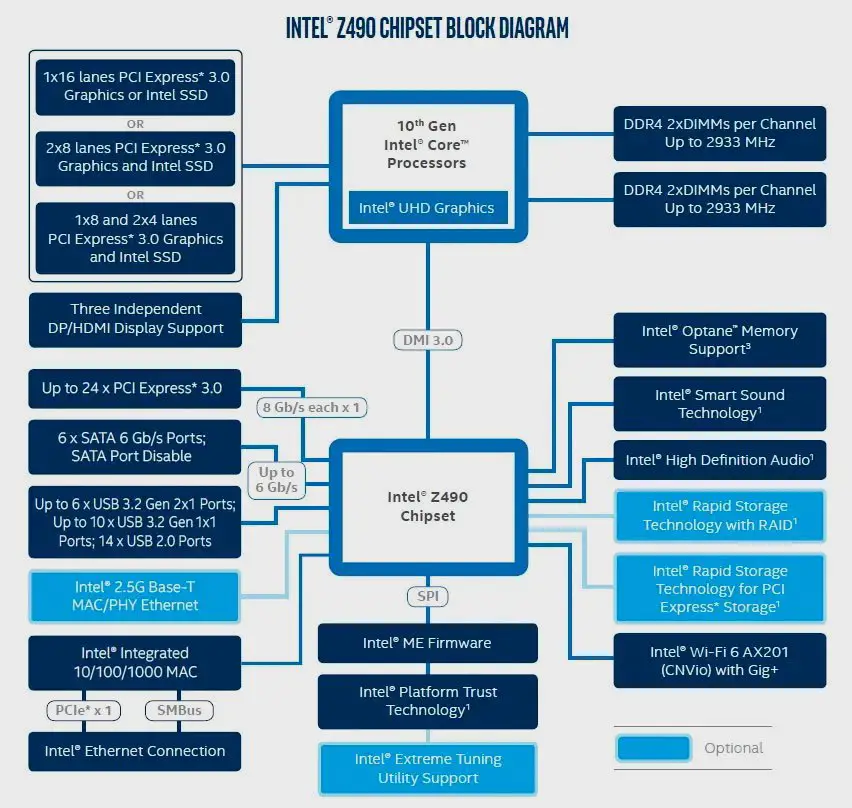
Regarding the characteristics of the Z490 chipset, in the attached image you can find all its keys. Overall it is almost a carbon copy of the Z390 chipset , as it has 24 PCIe Gen 3 lanes, six SATA III ports, six USB 3.2 Gen 2 ports, ten USB 3.2 gen 1 port, and fourteen USB 2.0 ports. Items marked in light blue are optional.
To take advantage of the Intel Core i9 10900K we need a motherboard with a Z490 chipset since otherwise, we will not be able to overclock it. However, keep in mind, as I already told you in the analysis of the Intel Core i5 10600K, that not all motherboards with a Z490 chipset are the same, and that to mount this processor you should look for models that have a solid and reliable power system, with good amperage and proper cooling.





