In this blog post, we will delve into the vulnerability of Android phones to fingerprint brute-force attacks. The original source of the news broadcasted on Bleeping Computer.
Understanding Fingerprint Brute-Force Attacks
Fingerprint brute-force attacks rely on repetitive attempts to crack the fingerprint authentication system on smartphones, aiming to gain unauthorized access and control over the device. These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in the security measures implemented on certain Android devices.
Exploiting Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
Researchers at Tencent Labs and Zhejiang University recently uncovered a new attack method known as ‘BrutePrint.’ By exploiting two zero-day vulnerabilities, Cancel-After-Match-Fail (CAMF) and Match-After-Lock (MAL), the researchers were able to bypass existing safeguards that protect against brute-force attacks on modern smartphones.
How BrutePrint Works
BrutePrint involves an attacker submitting an unlimited number of fingerprint images to the targeted device until a match is found with a user-defined fingerprint. Physical access to the device is necessary to launch this attack, along with access to a fingerprint database, which can be obtained from academic datasets or biometric data leaks. The cost of the required equipment is approximately $15.
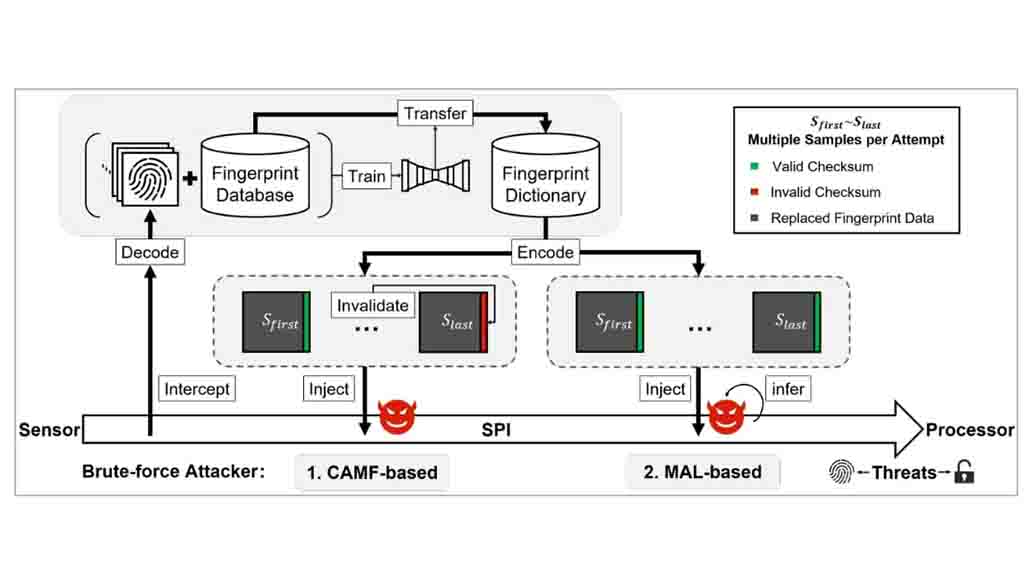
Manipulating Authentication Mechanisms
Unlike password cracking, fingerprint authentication relies on a reference threshold instead of a specific value. Attackers can manipulate the False Acceptance Rate (FAR) to increase the acceptance threshold and facilitate easier matches. BrutePrint manipulates the multi-sampling and error-canceling mechanisms of fingerprint authentication on smartphones by exploiting the CAMF vulnerability.
Overcoming Lockout Modes
The MAL flaw allows attackers to deduce authentication results of fingerprint images, even when the device is in “lockout mode.” Lockout mode is activated after a certain number of consecutive failed unlock attempts. However, the MAL vulnerability helps bypass this restriction, enabling the attackers to continue their brute-force attempts.
The Impact and Mitigation
The BrutePrint attack was tested against ten popular smartphone models, revealing that all Android and HarmonyOS (Huawei) devices were vulnerable to unlimited attempts, while iOS devices allowed for ten additional attempts. This vulnerability highlights the need for stronger security measures on Android devices to protect against fingerprint brute-force attacks.

Safeguarding Your Device: Protecting Against Fingerprint Brute-Force Attacks
Vulnerability of Android phones to fingerprint brute-force attacks raises concerns regarding user privacy and device security. It is crucial for device manufacturers and software developers to address these vulnerabilities by implementing robust security measures and regular software updates.
By understanding the potential risks associated with fingerprint authentication and staying vigilant about device security, users can mitigate the impact of such attacks and safeguard their personal information.
In the past months, we have also prepared an article about a Nexus Android Trojan infiltrating crypto wallets regarding the security problems of Smartphones, I suggest you check it out as well.