The artificial intelligence system known as Google Muse AI was officially unveiled today. Based on its use of parallel decoding and a small, discrete latent space, the new text-to-image transformer model claims to be faster than existing alternatives. The creators of Google Muse AI claim that their creation can generate photographs at a level of quality that is comparable to the best of the best.
We present Muse, a text-to-image Transformer model that achieves state-of-the-art image generation performance while being significantly more efficient than diffusion or autoregressive models.
Google Muse AI team
What is Google Muse AI?
The team claims that Google Muse AI is a big improvement over previous text-to-image transformer models like Imagen and DALL-E 2. Muse uses a big language model’s text embedding to be trained on a masked modeling job in discrete token space (LLM).

Muse is capable of recognizing tokens in images that have been disguised at will. Due to its use of discrete tokens and decreased sample size requirements, Muse promises to beat pixel-space diffusion models like Imagen and DALL-E 2. The model generates a free zero-shot, mask-free edit by repeatedly resampling image tokens in response to a prompt.
Based on MUSE‘s benchmarks, Muse’s inference times are significantly lower than those of competing models.
| Model | Resolution | Inference Time (↓) |
| Stable Diffusion 1.4 | 512×512 | 3.7s |
| Parti-3B | 256×256 | 6.4s |
| Imagen | 256×256 | 9.1s |
| Imagen | 1024×1024 | 13.3s |
| Muse-3B | 256×256 | 0.5s |
| Muse-3B | 512×512 | 1.3s |
Unlike Parti and other autoregressive models, Muse makes advantage of parallel decoding. To produce high-quality images and recognize visual concepts like objects, their spatial relationships, stance, cardinality, and so on, an LLM that has already been taught has to understand English at a granular level. The model doesn’t have to be flipped for Muse to support inpainting, outpainting, and mask-free editing.

Google Muse AI features
Muse is a quick, cutting-edge model for generating and altering images from text, and it has several useful features, including:
- Text-to-image generation
- In reaction to textual inputs, Google’s artificial intelligence (AI) Muse swiftly generates high-quality visuals (1.3s for 512×512 resolution or 0.5s for 256×256 resolution on TPUv4).

- Zero-shot, mask-free editing
- The Google Muse AI model gives us free zero-shot, mask-free editing by repeatedly sampling image tokens in response to a textual instruction.

- When altering an image, mask-free editing allows you to manipulate several objects with a simple text prompt.

- Zero-shot Inpainting/Outpainting
- Google’s Muse AI is free, and it comes with mask-based editing features (inpainting and outpainting). By applying a mask to an edit, it becomes functionally equivalent to a new generation.
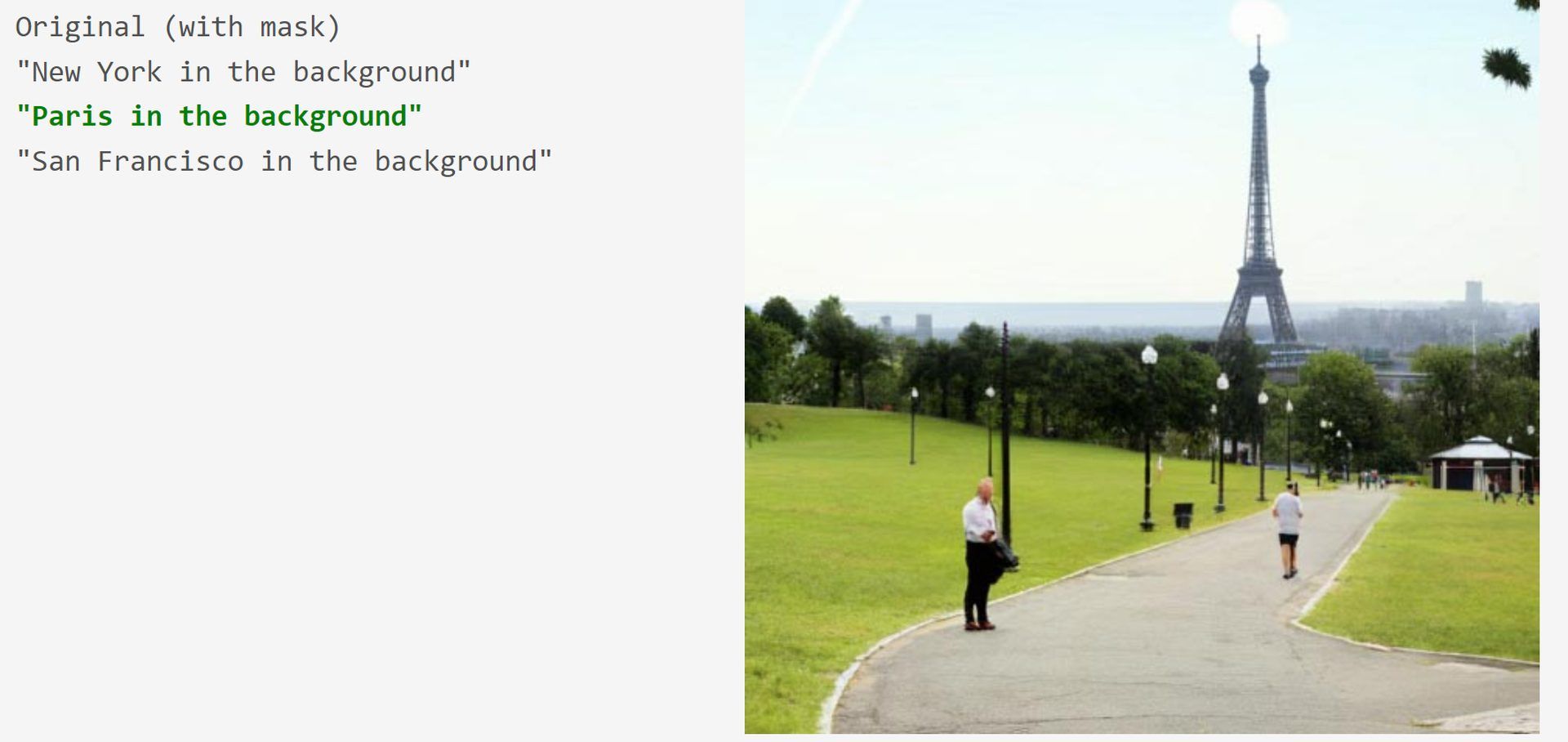
Check out the best AI tweet generators that will help you tweet like Elon Musk.
Google Muse AI model details
You can check Google’s Muse AI’s training flow down below:
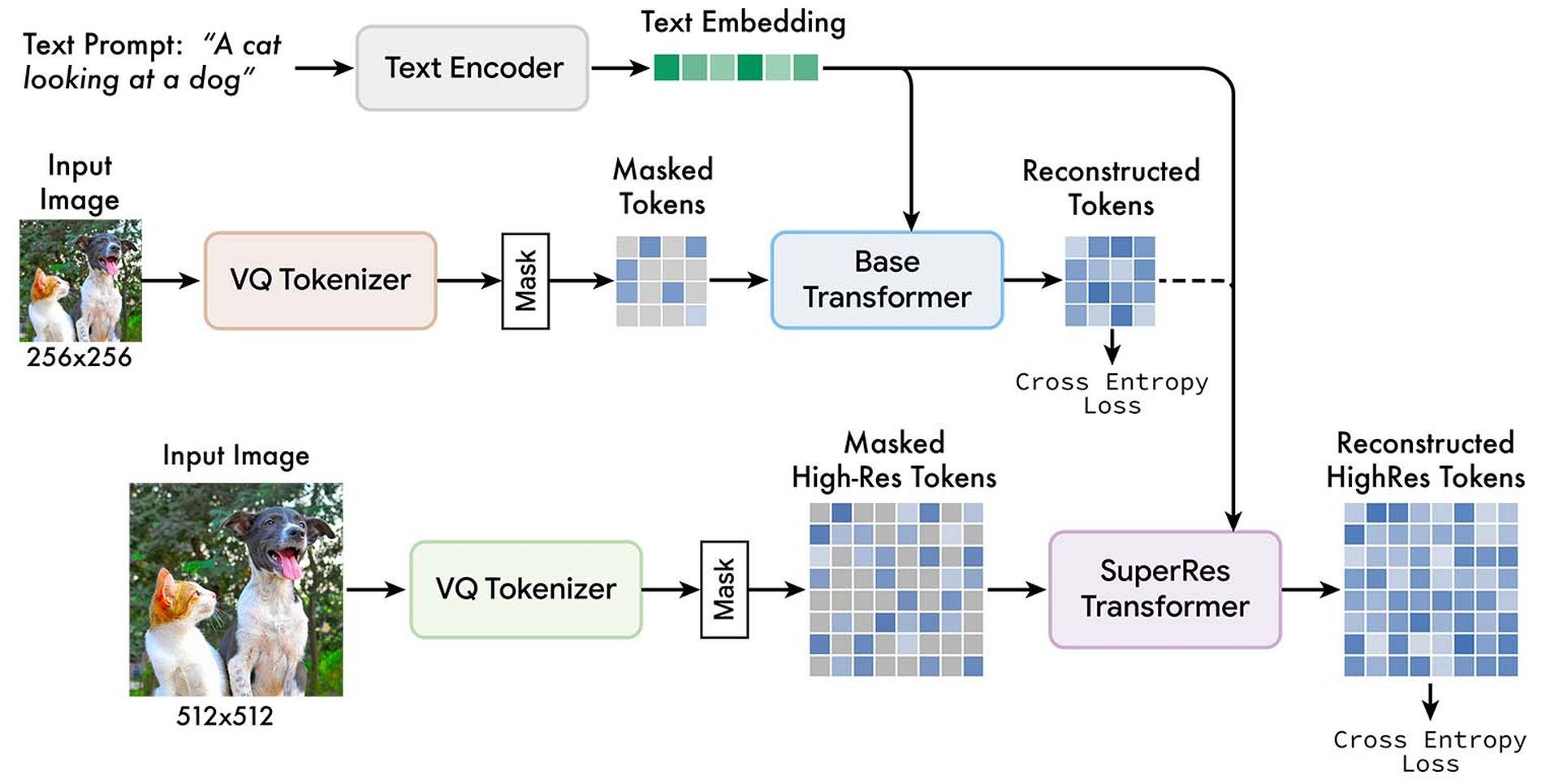
Two different VQGAN tokenizer networks are used by the Google team, one for low-quality photographs and one for high-resolution images. Low-resolution (“base”) and high-resolution (“superres”) transformers are trained with the unmasked tokens and T5 text embeddings to predict the masked tokens.
For more detailed information about Google Muse AI, click here.
AI tools we have explained
Although some say “no to AI generated images,” almost every day a new AI tool comes into our lives, such as:
- Poised AI
- Caktus AI
- OpenAI Point-E
- Uberduck AI
- QQ Different Dimension Me
- MyHeritage AI Time Machine
- Meta’s Cicero AI
- Notion AI
- Meta Galactica AI
- NovelAI
- Make-A-Video Meta AI
- DALL-E 2
- Wombo Dream
- Google’s DreamBooth AI
- Stable Diffusion
Stay tuned for more!





