Microsoft Defender Antivirus is a malware-fighting tool and its background process is the “Antimalware Service Executable.” Both of which comes installed by default in Windows 10. This software, sometimes referred to as MsMpEng.exe, is part of the Windows operating system. In this article, we will dive in and explain all that is to know about this Windows process.
What is Antimalware Service Executable?
Windows Defender is a free antivirus program that protects Windows 10 computers from malware and other threats. It’s the replacement for Microsoft Security Essentials. This ensures that all Windows 10 users have an antivirus program installed and running, even if they haven’t opted in to install one. If you have out-of-date antivirus software installed on your PC, Windows 10 will deactivate it and automatically switch you over to Microsoft Defender. The same anti-malware software is included in Windows 11.
The Antimalware Service Executable is Microsoft Defender’s background service, which runs in the background at all times. It’s in charge of malware checks when you access files, performing background system scans to look for harmful software, provisioning antivirus definition upgrades, and anything else a security program like Defender needs to do.
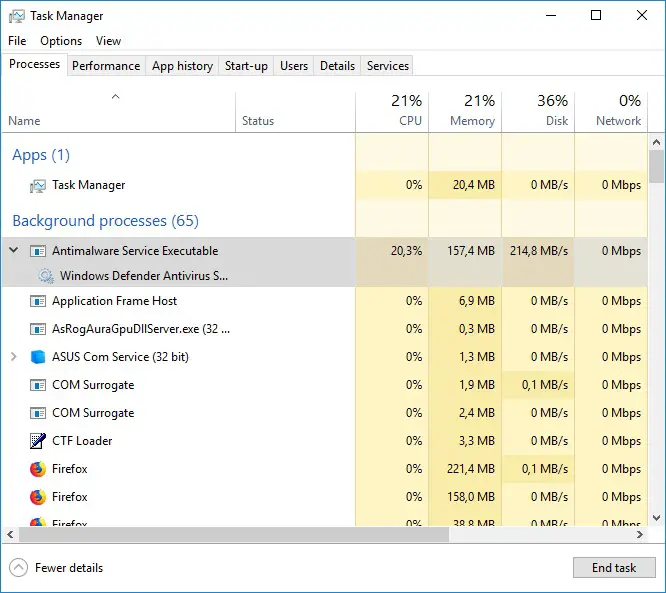
The filename of the process is MsMpEng.exe, which you’ll find on the Details tab in Task Manager. You may use the Windows Security application that comes with Windows 10 and Windows 11 to configure Microsoft Defender, run scans, and look at its scan history. This program was formerly known as the “Windows Defender Security Center.”
To start the program, open the “Windows Security” Start menu shortcut. You can also choose “View Security Dashboard” from the shield icon in your notification area, or go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Security > Open Windows Security.”
Why is Antimalware Service Executable using CPU?
It’s possible that the Antimalware Service Executable process is utilizing a lot of CPU and disk resources. Microsoft Defender, like other antivirus programs, uses background scans on your computer to check for malware.
It also checks files as soon as you open them, and it automatically notifies you about new malware infections. This CPU usage might also indicate that an upgrade is being installed or that you just opened a quite large file. Microsoft Defender requires some additional time to analyze the data.

The majority of Windows Defender’s background scans are performed only when your computer is sitting idle and isn’t being utilized. Even while you’re using your PC, it may utilize CPU resources to download updates or scan documents. However, the background scans shouldn’t be running when you’re using your PC.
This is entirely natural with any antivirus program, as they all need to utilize system resources to analyze your PC and keep you safe.
Can I disable Antimalware Service Executable?
We don’t recommend turning off the Microsoft Defender antivirus software or Antimalware Service Executable if you don’t already have another antivirus program. In fact, you can’t deactivate it permanently. You can access the Windows Security application from your Start menu, and then select “Virus & Threat Protection,” then “Manage Settings” under Virus & Threat protection settings. Select “Real-Time Protection” and disable it. However, this is only a stopgap measure, and Microsoft Defender will re-activate once other antivirus applications are no longer detected.
Despite what you may read on the web, Defender runs its scans as a system maintenance function that you cannot turn off. Disabling tasks in the Task Scheduler will not help. It will only be permanently stopped if you install another antivirus program to take its place.

If you have another antivirus program installed and active, Microsoft Defender will automatically be disabled and placed out of the way. If you go to Windows Security > Virus & threat protection, you’ll encounter a notice stating “You’re using other antivirus software.” This means Windows Defender is turned off. The process may continue to run in the background, but it should not utilize CPU or disk resources to scan your system.
However, there is a way to use both your current antivirus software and Microsoft Defender at the same time. You can expand “Microsoft Defender Antivirus options” on this screen and enable “Periodic scanning.” Even while you’re using another antivirus program, Defender will run background scans in the background, giving a second opinion that may find what your main antivirus might have missed.
If you discover Microsoft Defender utilizing CPU even though you have other antivirus applications installed, go here and make sure the Periodic scanning option is set to “Off.” If you don’t mind, you can turn Periodic scanning on. It’s another layer of protection and security. This function, however, is disabled by default.
Is Antimalware Service Executable a virus?
There haven’t been any reports of viruses pretending to be the Antimalware Service Executable process. Because Microsoft Defender is itself an antivirus, it should be able to stop any malware from attempting this. It’s common for Defender to be running while you’re using Windows and have Microsoft Defender switched on.
If you’re really concerned, you may always perform a scan with another antivirus software to ensure that no harmful programs are installed on your computer.