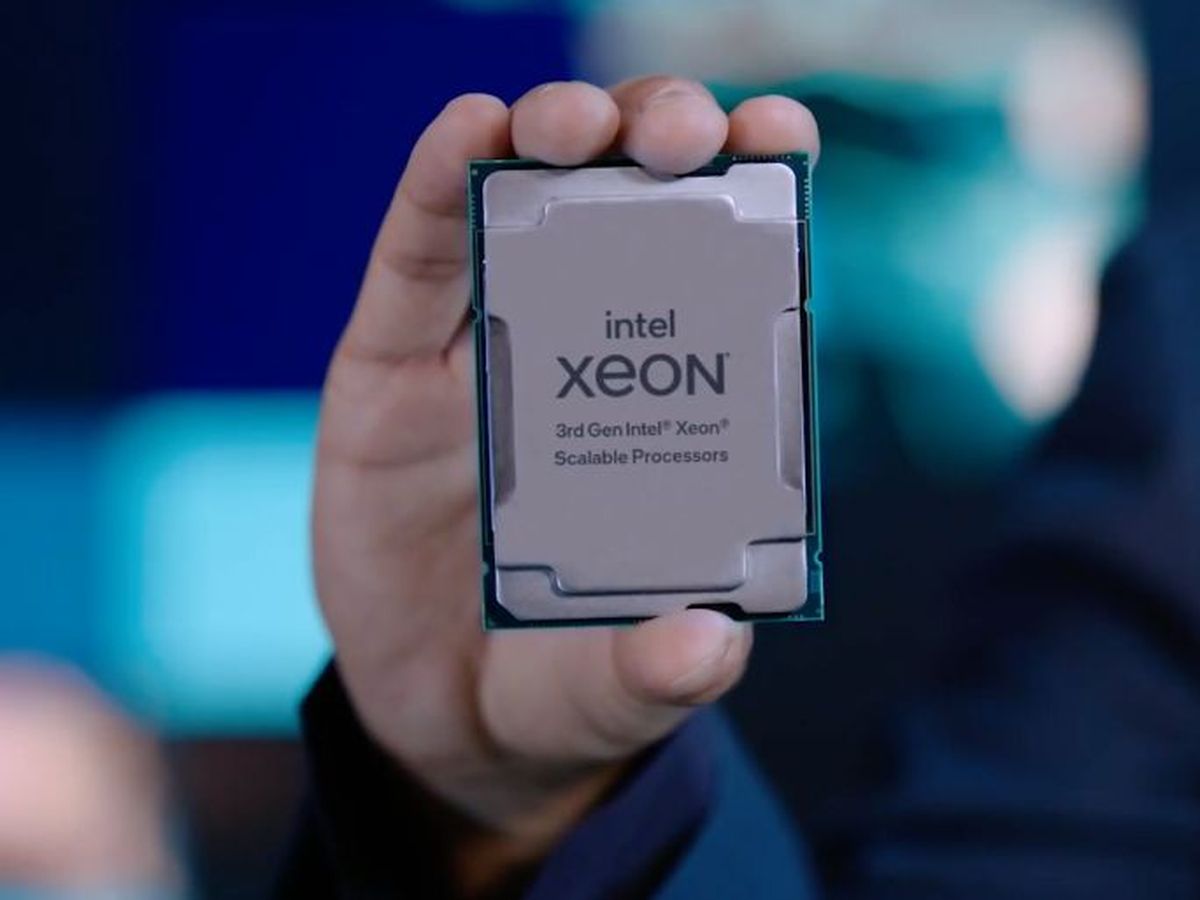
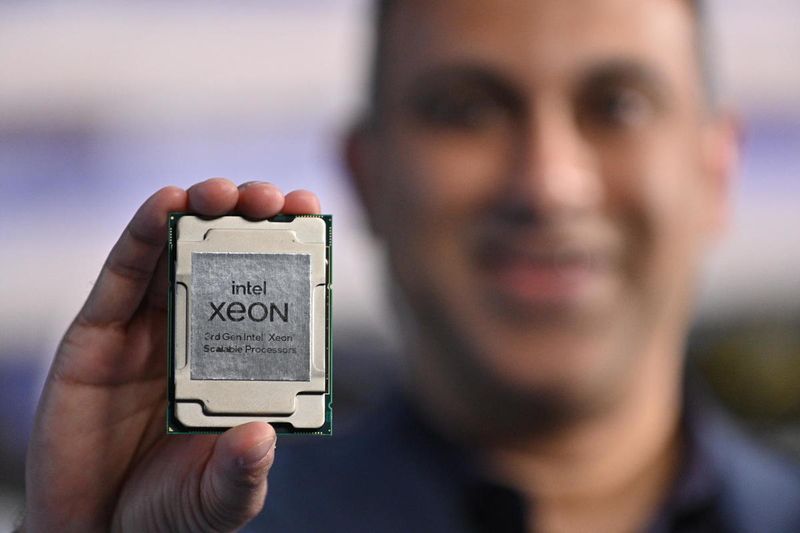
The third generation of Intel Xeon Scalable processors, the latest hardware product that Intel offers to data centers, 5G mobile networks, and for the most advanced technological infrastructures, has already seen the light of day. The presentation was made by Navin Shenoy, Intel’s executive vice president, and general manager of the Intel Xeon Scalable Group.
The third generation of Intel Xeon Scalable processors, Intel’s latest hardware product for data centers, 5G mobile networks, and advanced technology infrastructures, has been released.
The presentation was made by Navin Shenoy, Intel executive vice president, and general manager of the Data Platforms Group; And Lisa Spelman, corporate vice president, and general manager of the Memory and Xeon Processors Group, in addition to the participation of Intel CEO Pat Gelsinger.
Third-generation Intel Xeon Scalable, Codenamed Ice Lake, is unveiling a new chapter in all areas where Intel is present, from servers and data centers to the Cloud.
It is clear that Intel wants to maintain its leadership position and added value by being able to provide companies with a complete set of solutions: CPU, network, memory, storage, storage, software, and, most especially in recent times, artificial intelligence accelerators.
Intel offers the IDM 2.0 (Integrated Device Manufacturing) Strategy to respond to the needs of its customers, at the base of which is the third generation of the Intel Xeon Scalable processor, capable of meeting the needs of public and private Clouds, decentralized and distributed data centers, with flexibility that combines hardware, software, and services.

What’s new in Intel Xeon Scalable in its third generation?
The latest generation of Xeon offers a 50% improvement over the previous generation, adding new features such as integrated artificial intelligence (the result of Intel’s efforts in this chapter since 2016) or Intel Crypto, acceleration for real-time code protection. A fast and flexible processor, secure and more efficient with solutions based on open standards.
The third generation of Xeon allows configurations of one, two, four, and up to eight sockets with up to 40 cores, sixty-four PCI, eight lines of DDRAM, and management of up to 64TB of storage.
The lower latency and bandwidth requirements make it possible to move the data processing architecture as close as possible to where it is needed. Here comes the decentralization of data processing, capable of approaching, with Intel Xeon, the production chain itself: Factories, companies, communications towers. This requires handling large data flows in real-time, which can be done through 5G communications technology, something that is integrated into the processor itself, with a 62% improvement over previous generations.
During 2020, confinement led to a significant increase in online traffic and content consumption, with Netflix, in particular, seeing its traffic rise by 61%, while overall streaming consumption increased by 600%. Only a flexible infrastructure can cope with these unexpected demands and deliver performance that is 50% higher than what previous systems and technologies were able to cope with. Xeon enables a simple, fast, and flexible migration to meet future user demands.