Meta AI opt-out (option) is a key concern for users of Facebook and Instagram as the company updates its privacy policy to utilize user posts and images for training its artificial intelligence (AI) models. This policy shift, aimed at enhancing services like the AI Creative Tool and AI chatbots, has sparked a significant conversation about data privacy and user rights. Here, we explore the implications and the steps users can take to manage their data effectively.
Starting June 26, 2024, Meta’s AI will analyze public posts, photos, and captions across Facebook and Instagram to improve its AI functionalities. This change follows Meta’s ongoing expansion of generative AI features, such as integrating AI personas and enhancing search capabilities with AI assistance on various platforms. While private messages remain untouched, the breadth of public content subjected to AI training raises concerns among users.
Meta AI Opt-Out and addressing data privacy concerns
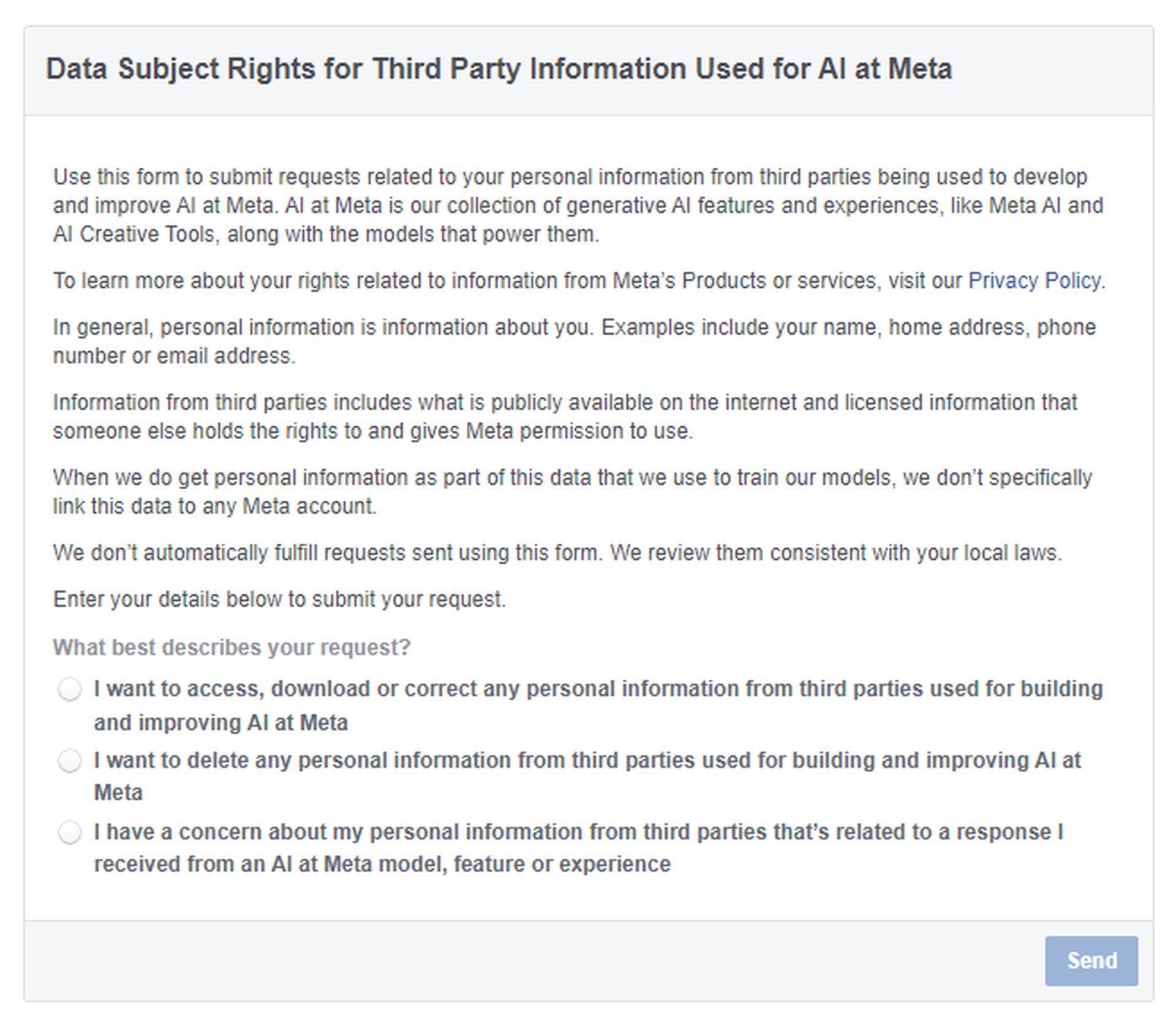
Meta AI opt-out assumes user consent unless explicitly objected to. Users in regions such as the EU and the UK, which are governed by stricter privacy regulations such as GDPR, have been informed and given the “right to object”. However, the process of objecting is seen as burdensome and potentially discourages many from taking action. To object, users need to go to a specific form on Facebook’s help page and provide their residence details, email address, and the reason for their objection. This mechanism ensures compliance with local privacy laws but has been criticized for being intentionally complicated.
Meta AI opt-out policies will use public posts, photos, and captions to enhance AI functionalities, including the AI Creative Tool and AI chatbots. This policy change is in line with Meta’s broader efforts to integrate AI more deeply into its platforms. By analyzing user-generated content, Meta aims to improve its AI capabilities and provide more personalized services. However, the use of public data for AI training without explicit user consent has raised privacy concerns among users.
1. I'm legit shocked by the design of @Meta's new notification informing us they want to use the content we post to train their AI models. It's intentionally designed to be highly awkward in order to minimise the number of users who will object to it. Let me break it down. pic.twitter.com/rhKNFt7CEu
— Tantacrul (@Tantacrul) May 26, 2024
Public posts, photos, and captions on Facebook and Instagram will be used for AI training, but private messages are excluded. This distinction is important for users who are particularly concerned about their private communications being accessed. Meta AI opt-out policy change reflects a trend in the tech industry where user data is increasingly leveraged to train and improve AI models. This practice is justified under the principle of “legitimate interest,” which allows companies to use data in ways that are deemed beneficial for both the company and its users.
Despite the exclusion of private messages, the broad use of public content has led to concerns about user privacy. Users are given the “right to object,” but the process to opt-out is not straightforward. Navigating the opt-out procedure can be challenging, and many users may find it difficult to complete the necessary steps to prevent their data from being used.
How to navigate user consent and objection
Meta AI opt-out policy assumes that users consent to the use of their public data unless they explicitly object. This approach places the responsibility on users to take action if they do not wish to participate. In regions like the EU and UK, where GDPR provides stricter privacy protections, users have been notified of their right to object. However, the process to opt-out has been criticized for being complex and difficult to navigate.
To object to the use of their data, users must fill out a form on Facebook’s help page. This form requires users to provide their residence details, email address, and a reason for their objection. While this process ensures compliance with local privacy laws, it has been designed in a way that may discourage users from completing it. Users must be proactive and thorough in filling out the form to ensure their objection is processed.
For users who are determined to prevent their data from being used, deleting their account is the most effective but harshest option. However, there are other ways to limit data sharing. Adjusting privacy settings and disabling “non-Meta activity” are steps users can take to control how their data is shared. These measures primarily affect third-party data sharing and do not fully prevent Meta from using user data internally. Users should be aware that even after opting out, some data may continue to be used in certain circumstances.
Understanding the broader context
Meta AI opt-out policy integration of user data for AI training is part of a larger trend in the tech industry. Companies like Meta are increasingly leveraging user-generated content to train and improve their AI models. This practice is seen as a way to enhance services and provide more personalized experiences for users. However, it also raises important questions about data privacy and user rights.
Meta AI opt-out justification for the use of public data for AI training is under the principle of “legitimate interest”. This means that the company believes the use of data will benefit both Meta and its users. For example, by analyzing public posts and photos, Meta can improve its AI tools, making them more accurate and useful. However, this justification has been met with skepticism by users who are concerned about their privacy.
Meta AI opt-out policy change highlights the importance of user awareness and proactive management of digital privacy. As companies continue to innovate and integrate AI into their services, users must stay informed about how their data is being used. Understanding the implications of privacy policies and taking steps to protect personal information is crucial in today’s digital age.

Managing your data moving forward
Meta AI opt-out means that users need to actively manage their privacy settings as these changes roll out. This policy update serves as a reminder of the evolving nature of digital privacy and the need for users to be vigilant. Users can navigate these changes more effectively by understanding the implications of Meta’s AI privacy policy and taking steps to protect their data.
Adjusting privacy settings and disabling “activity off Meta” are practical steps that users can take to manage their data. While these measures may not completely prevent Meta from using user data, they can help limit the amount of information that is shared. Users should regularly review their privacy settings and make adjustments as necessary to protect their personal information.
The key to navigating the Meta AI opt-out privacy policy is to stay informed and proactive. Users can take more control over their digital privacy by understanding the policy and taking steps to manage their data. This policy change underscores the importance of user awareness and proactive management in an increasingly data-driven world.
Featured image credit: Muhammad Asyfaul / Unsplash





