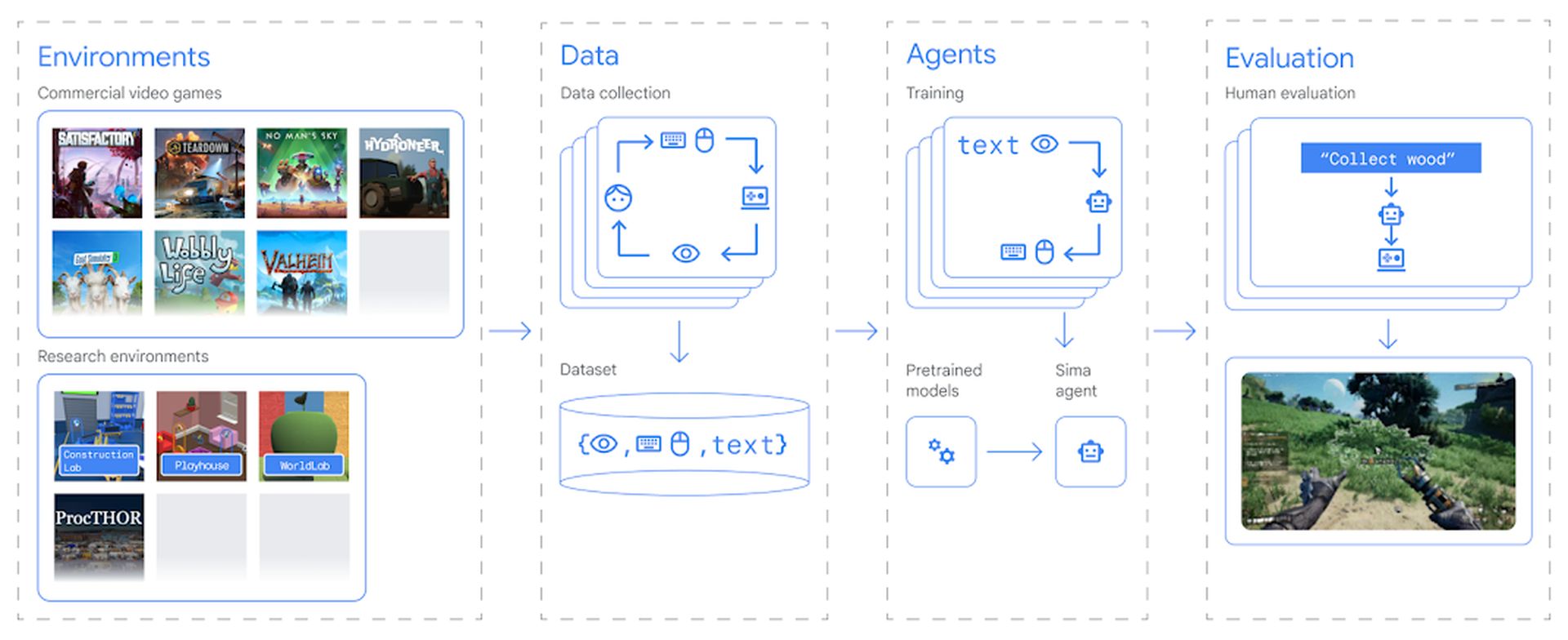
Google DeepMind’s recent innovation, SIMA (Scalable Instructable Multiworld Agent), is a major development for creating a generalist AI for 3D virtual environments.
Unlike traditional AI programmed for specific tasks within a single game, SIMA is a versatile learner. It can process both visual information and natural language instructions, allowing it to understand and complete tasks in diverse virtual worlds.
This adaptability opens doors to not only revolutionize our interaction with virtual spaces but also potentially address real-world challenges.
What makes SIMA so special?
Imagine giving an AI instructions like “find water” or “pick up iron ore.” SIMA accomplishes this feat by utilizing large language models to comprehend natural language commands.
Additionally, it employs convolutional neural networks to analyze the virtual environment visually, giving it a well-rounded understanding of the situation.
Traditionally, AI excels at mastering one specific task within a limited environment. SIMA breaks this mold.
By being trained on a variety of games, ranging from survival adventures like Valheim to complex construction simulations, it learns to adapt to new environments and situations quickly. This allows it to tackle unseen challenges within the virtual world.
Learning also doesn’t stop for it. It can break down complex instructions into smaller, more manageable steps. This, combined with hierarchical reinforcement learning, allows it to refine its approach and develop new skills.
Furthermore, by observing its actions and the resulting changes in the environment, it can generate its own training data. This self-supervision empowers it to continuously learn and improve in new situations.
Want to learn more about how SIMA does its magic? Check out the research paper.
OK but where is the catch?
The fact that SIMA can understand and carry out instructions is a major step towards AI that can assist us in the real world.
Video games are a great testing ground for AI development. They provide safe spaces to experiment, and their clear goals and immediate feedback help it learn. As SIMA explores ever more complex virtual worlds, the algorithms that power it get smarter. This could lead to AI that’s adaptable, capable of following commands, and focused on achieving goals outside of the game world.
From pixels to possibilities
The potential applications of SIMA extend far beyond the realm of gaming. Imagine AI-powered robots, less susceptible to fatigue or error, handling dangerous mining tasks, potentially saving lives.
Similarly, the ability to find water in games like Valheim translates to real-world applications in regions facing water scarcity.
By learning through the vast datasets and challenges presented in video games, AI can be equipped to address real-world issues like resource management and safety concerns.
SIMA’s development highlights the immense potential of AI, not just for entertainment, but for building a better future.
Thinking about how long has AI been helping us makes us wonder: What more can this technology, which has changed our lives in such a short time, show us?
Featured image credit: Google DeepMind.





