Since you hear it so often at CES 2024, we thought we should answer your question: what is spatial computing?
Spatial computing is a term that has gained significant attention in recent years, particularly in the tech industry. It refers to a broad range of technologies that enable people to interact with computers in more natural and immersive ways, moving beyond traditional screens and keyboards. Spatial computing is all about blending the physical and digital worlds to create seamless and interactive experiences.
But what is spatial computing exactly? Let us explain.

What is spatial computing?
So, what is spatial computing?
Spatial computing is a broad term encompassing technologies that blend the physical and digital worlds, allowing for interaction with computers in more natural and immersive ways. Think beyond traditional screens and keyboards!
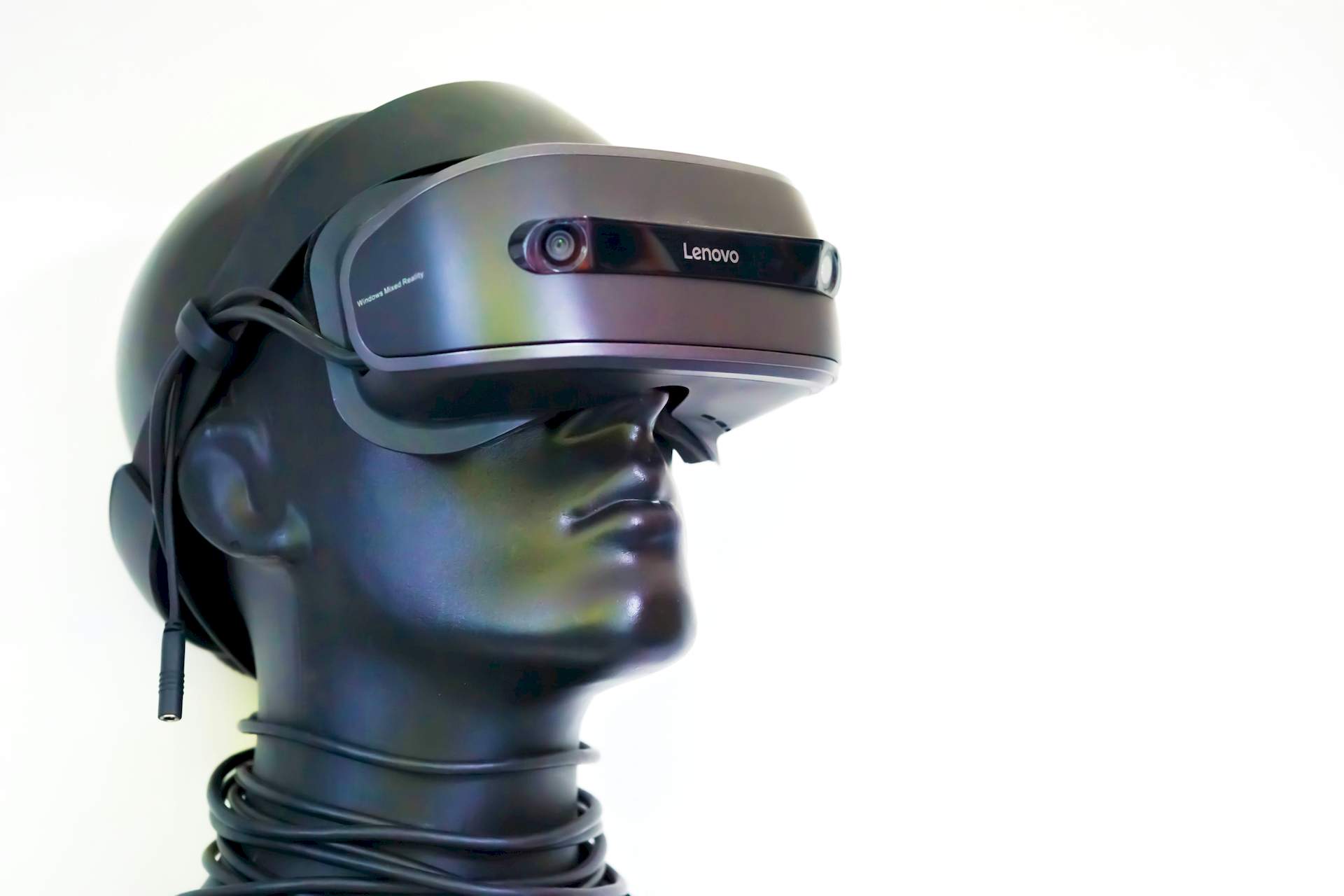
At its heart, spatial computing involves understanding and interacting with our physical environment using devices like headsets, glasses, AR/VR displays, and sophisticated sensors. It aims to seamlessly integrate digital elements into our physical space, like virtual objects overlaid on real-world scenery.
To answer what is spatial computing, we must first explain the key technologies behind it:
Augmented Reality (AR): Overlays digital information onto the real world, like navigation arrows on your windshield or virtual furniture in your living room.
- Virtual Reality (VR): Creates a completely immersive virtual environment, blocking out the real world
- Mixed Reality (MR): Combines AR and VR, seamlessly blending virtual and real elements in the same space
- 3D sensing and object recognition: Allows devices to understand the shape, location, and movement of objects in the physical world
- Spatial audio: Creates realistic sound effects that move around you based on your head position, enhancing immersion

So with all these technologies and spatial computing in general, Apple Vision Pro‘s technology has various applications.
With spatial computing, users can immerse themselves in virtual reality (VR), where they explore fantastical worlds, interact with virtual characters in augmented reality (AR), or engage in battles within mixed reality environments.
For education and training purposes, the technology offers the opportunity to delve into historical events, practice complex procedures, and collaborate with students from around the world in virtual classrooms.
As for design and architecture, spatial computing allows users to visualize 3D models of buildings within real-world spaces, collaborate on designs remotely, and experience the visual impact of renovations before construction begins.
In healthcare and surgery, doctors can leverage the technology to visualize patient data directly on the body, engage in realistic simulations for training purposes, and even conduct remote surgery using robots controlled through AR/VR interfaces.
Lastly, for manufacturing and maintenance, the technology provides workers with real-time instructions overlaid on machinery, the ability to troubleshoot complex systems remotely with AR assistance, and the opportunity to collaborate with experts located elsewhere.

Is spatial computing the same as IoT?
Now that we are done with explaining what is spatial computing, it is a good time to compare it with a pretty close technology, IoT.
Spatial computing and IoT (Internet of Things) are two related but distinct technologies. While they share some similarities, they have different focuses, technologies, applications, and goals.
Spatial computing is concerned with interacting with the physical world through digital elements. It utilizes technologies like augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), mixed reality (MR), 3D sensing, and spatial audio to create immersive and interactive experiences that blend the digital and physical worlds. Spatial computing has a wide range of applications, including gaming, education, design, healthcare, and manufacturing. Its primary goal is to create immersive experiences that enhance our interaction with the physical world.
On the other hand, IoT focuses on connecting devices and objects to the internet for data collection and remote control. IoT uses sensors, actuators, communication protocols, and cloud platforms to collect and analyze data from connected devices. Its applications include smart homes, cities, factories, healthcare, and more. The primary goal of IoT is to automate and optimize processes by collecting and analyzing data from connected devices.

Although spatial computing and IoT have some similarities, there are significant differences between them. Spatial computing focuses on interaction and experience, while IoT focuses on data and automation. Spatial computing uses AR/VR, MR, and 3D sensing, while IoT uses sensors, actuators, and communication protocols. Spatial computing has broader applications in various fields, while IoT focuses on specific areas like smart homes, cities, and factories.
Ultimately, spatial computing aims to create immersive experiences, while IoT aims to automate and optimize processes.
Featured image credit: James Yarema/Unsplash.