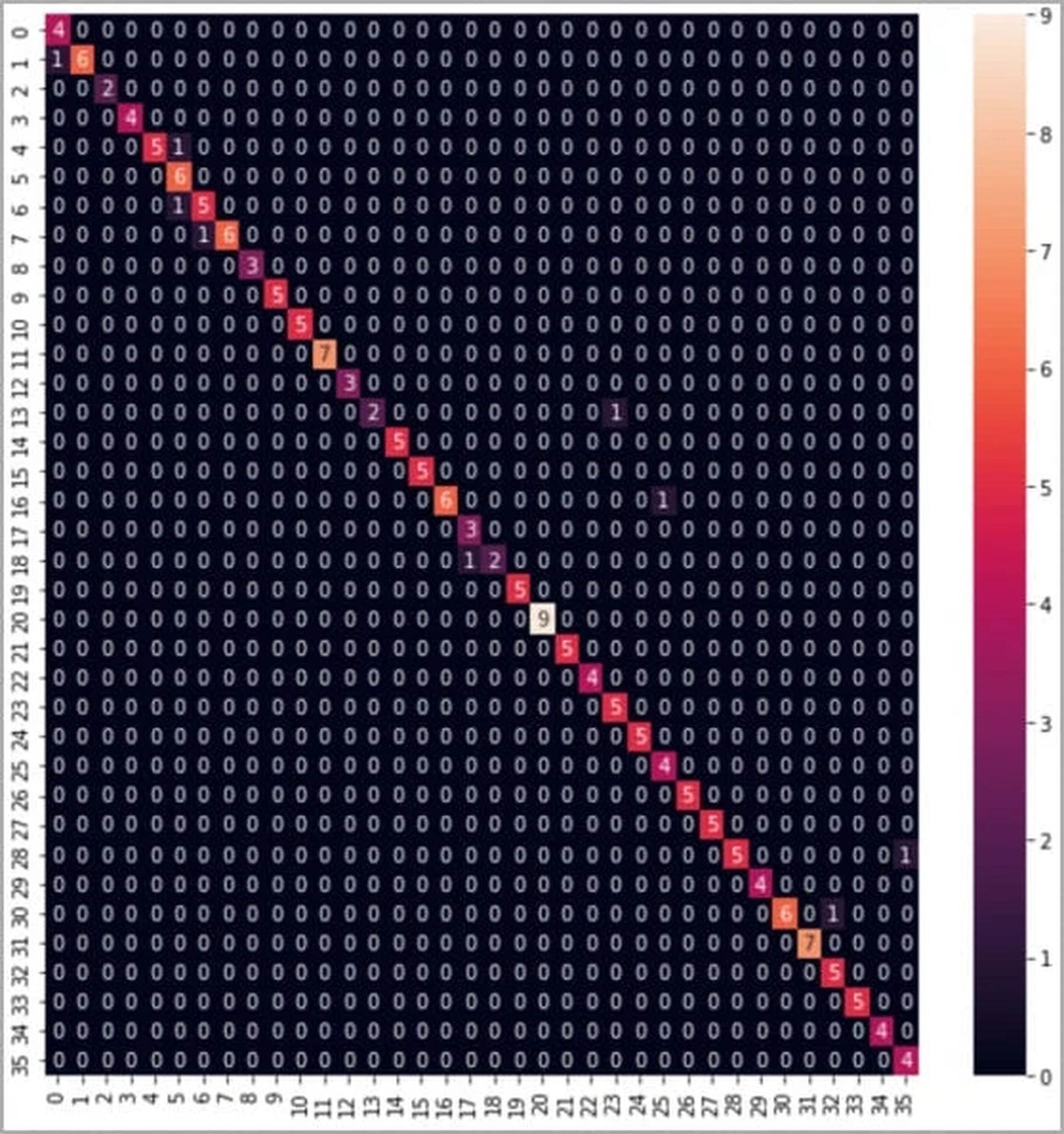
Advancements in technology continue to reshape the landscape of cybersecurity, introducing both novel opportunities and unforeseen risks. A team of researchers hailing from British universities has demonstrated an alarming exploit that leverages sound waves to pilfer sensitive data from keyboard keystrokes. The technique, which employs a deep learning model, boasts an impressive accuracy rate of 95%.
The experiment was rooted in the recognition that sound waves generated by keyboard presses could be harnessed to discern the actual keystrokes. The researchers embarked on a pioneering journey that showcased the potential dangers of acoustic-based attacks on data security.
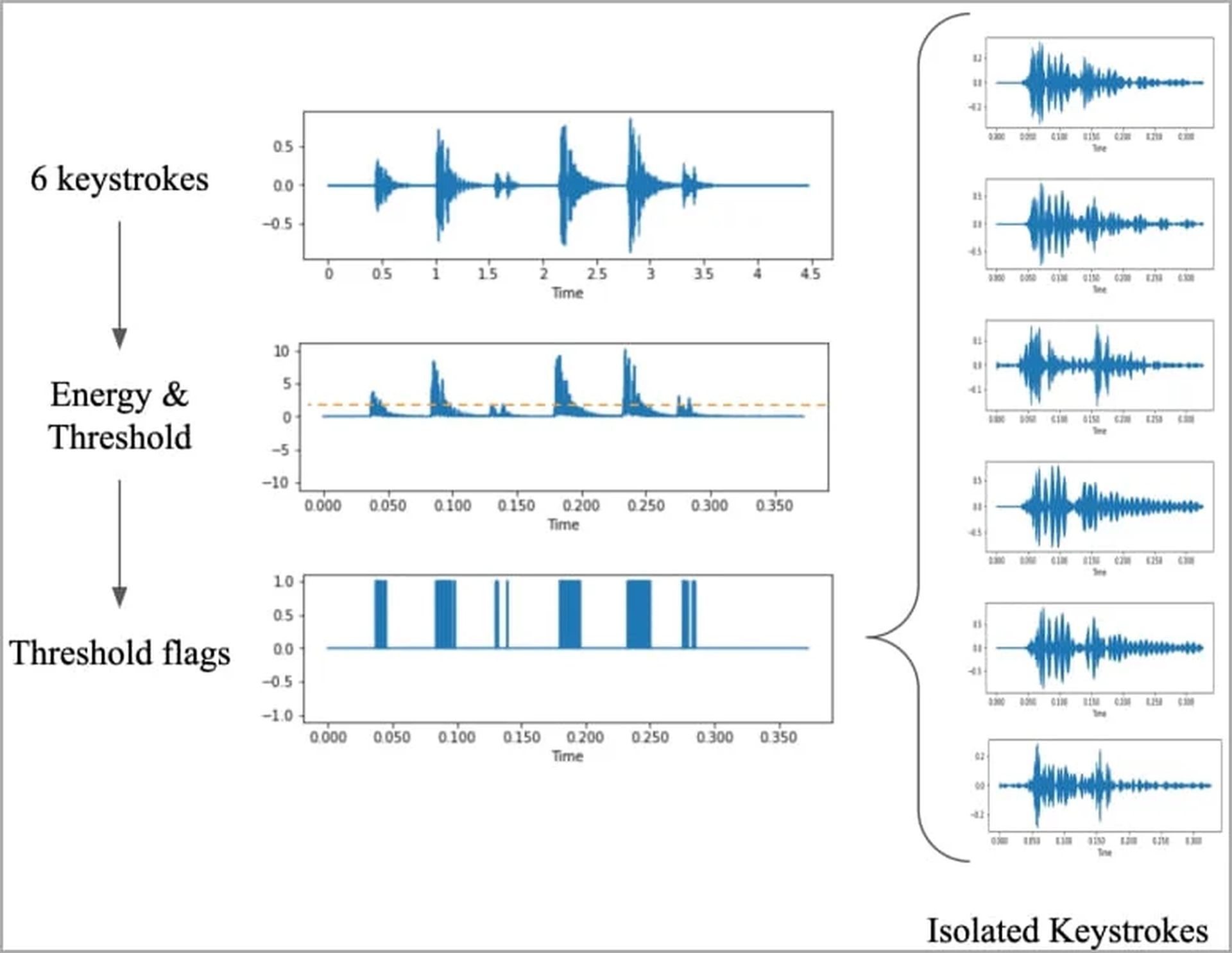
The methodology of the research
At the core of this audacious exploit lies the intricate interplay between sound, machine learning, and data extraction. The research team employed a range of devices, from laptops to smartphones, to capture the unique sound profiles of keystrokes. A total of 36 keys were pressed 25 times each on a modern MacBook Pro, while the resulting audio signals were meticulously recorded.
The captured sound data underwent a series of processing steps, eventually transforming into visual representations such as waveforms and spectrograms. These visualizations showcased distinctive variations for each keystroke, paving the way for the development of a powerful image classifier, named ‘CoAtNet.’
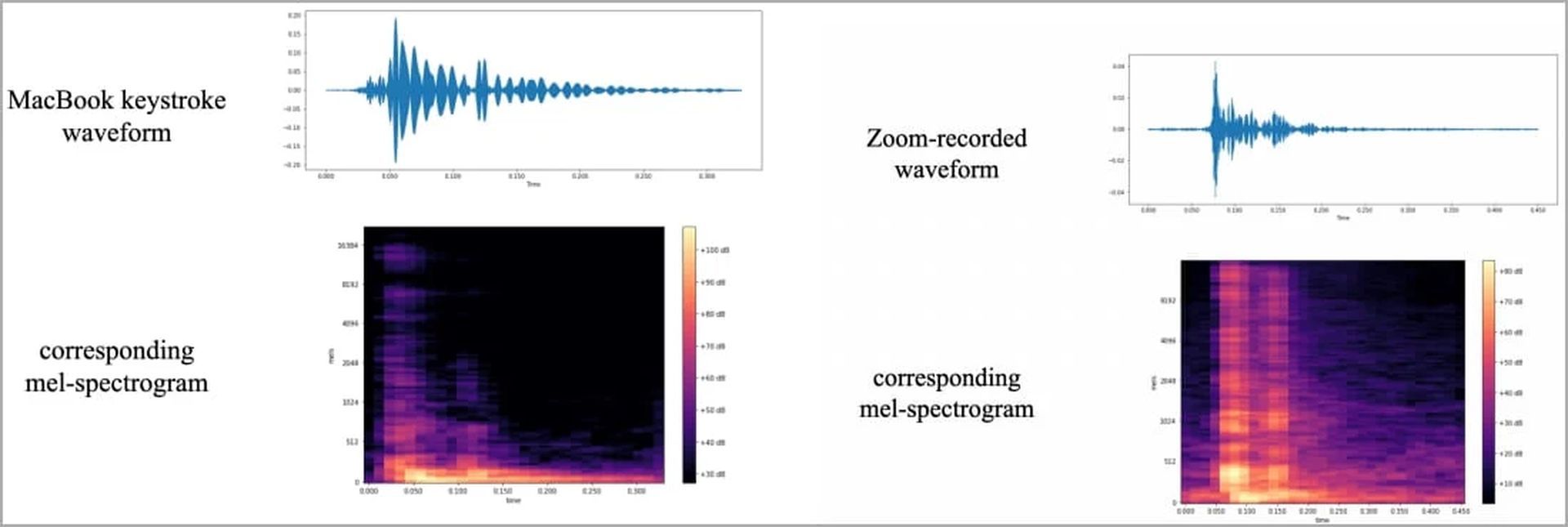
The implications of the results
The implications of this research are profound and unsettling. Acoustic-based attacks sidestep traditional security measures, exploiting the ubiquity of microphone-equipped devices to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information. This novel approach is particularly troubling as it can potentially expose personal data including passwords, conversations, messages, and other confidential data to malicious actors.
Traditional side-channel attacks typically necessitate specific conditions and are often bound by data rate and distance constraints. However, acoustic attacks have ushered in a new era of simplicity and efficiency, capitalizing on the abundance of devices capable of recording high-quality audio.
Mitigation strategies
As this groundbreaking research underscores the critical importance of safeguarding against acoustic attacks, it becomes essential to explore mitigation strategies that users can employ to protect their data.
- Altered typing styles: The study recommends users consider altering their typing styles to obfuscate the acoustic signature of their keystrokes.
- Randomized passwords: Using randomized passwords can disrupt the pattern recognition capabilities of acoustic-based attackers.
- Software-based defenses: Employing software that mimics keystroke sounds, generating white noise, or utilizing software-based audio filters can potentially thwart data theft.
- Biometric authentication: Implementing biometric authentication methods can enhance security by adding an additional layer of identity verification.
- Password managers: Relying on password managers can minimize the need for manual entry of sensitive information, reducing exposure to acoustic attacks.
In a world characterized by the rapid evolution of technology, security concerns continue to evolve as well. The research serves as a stark reminder that innovative methods of data theft constantly emerge, necessitating a proactive and adaptive approach to cybersecurity. As the digital realm advances, so too must our defenses against those who seek to exploit its vulnerabilities.
In addition to the research from British universities, there have been growing developments of AI models that are focused on data theft and hacking practices. Last month, an AI model focused on data theft with the name FraudGPT emerged, as well as an AI model named WormgGPT, which claims to have no boundaries whatsoever, allowing illegal and unethical conversations.
If you wish to be more prepared regarding the ongoing developments in deep learning and AI models, make sure to check out our article on how to beware of widespread ChatGPT scams.
Featured image credit: Sergi Kabrera / Unsplash





