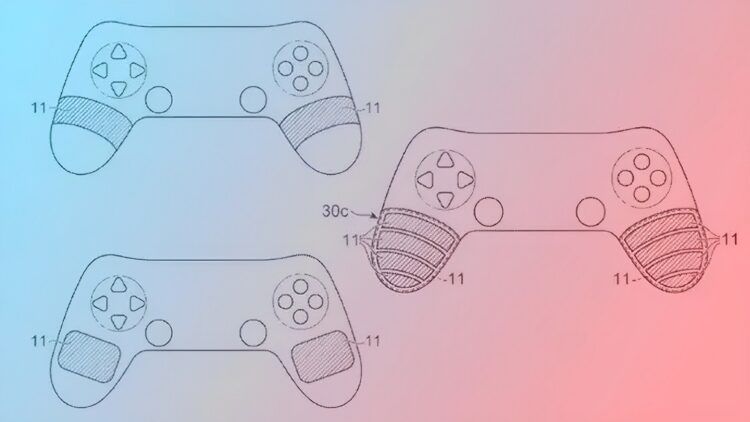
The upcoming new PlayStation controller may have new Haptic Feedback features, such as the capacity to adjust the temperature in response to games, according to a recent Sony patent.
One of the numerous features described in a patent for a controller constructed, at least in part, of a more gel-like material than the present plastic is the ability to simulate either hot or cold sensations for the user. With the news of the new PlayStation Handheld being on its way, Sony really seems to step its game up a bit.
What does the new PlayStation controller patent include?
The temperature of the upcoming new PlayStation controller may vary depending on an object or environment in the game, according to a recent Sony patent. During the past month or two, Sony has filed a number of these types of patents, many of which provide novel ideas for how the console manufacturer may enhance PlayStation’s quality-of-life features or make gameplay feel more immersive. There are patents for more understandable parental controls, a method to prevent children using PlayStation VR from accessing adult content, and even a “virtual dojo” to assist gamers to develop their skills, among others.
Regarding the Haptic Feedback features on heat, “The elastic member may include such a material as gel whose elastic modulus or hardness changes under heat,” Sony said, “to control the elastic modulus or hardness by change of the temperature with the above temperature control apparatus.”
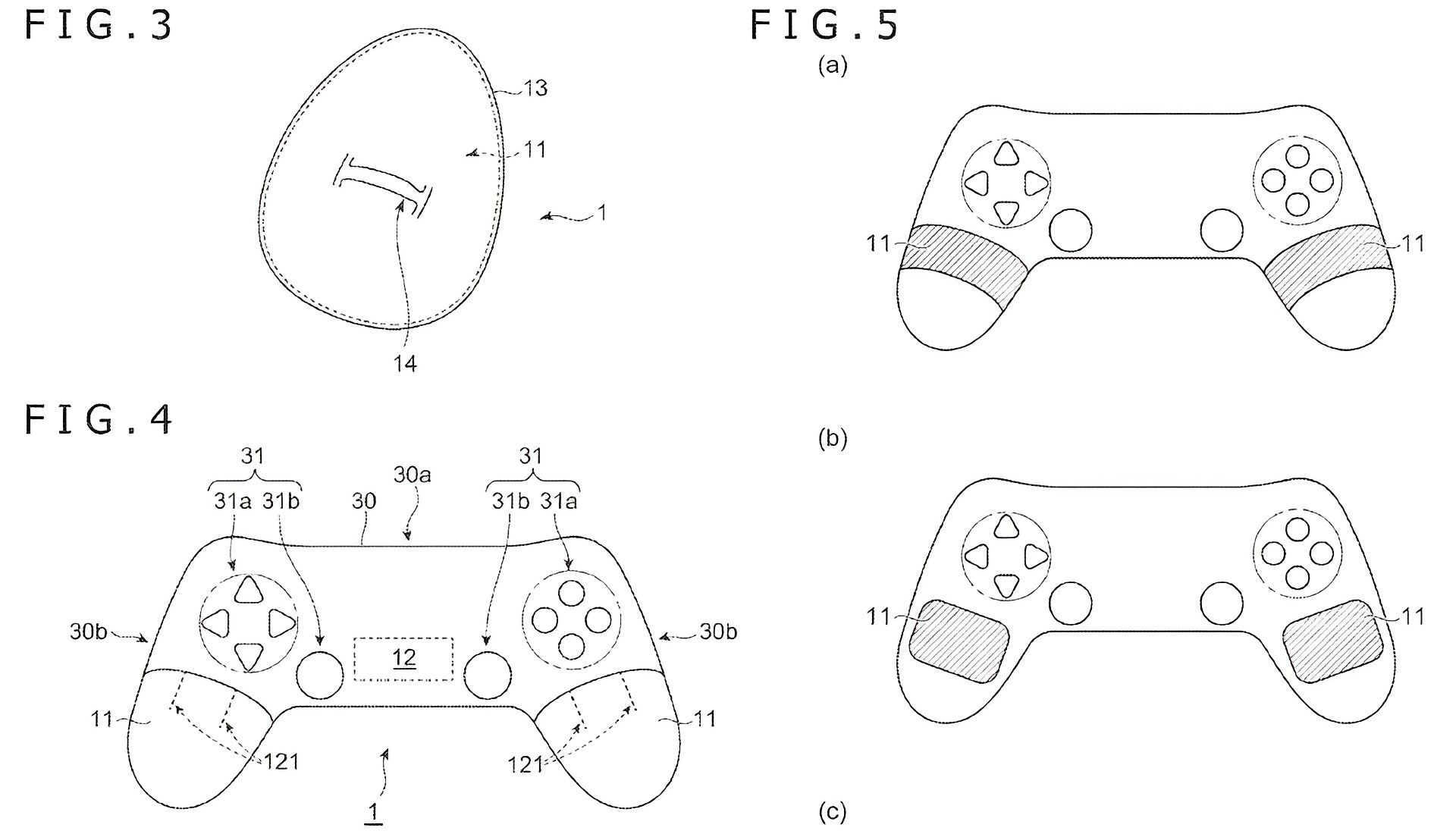
“The temperature control apparatus may be controlled such that the larger the amount of deformation, the higher the temperature becomes,” Sony also wrote. “This allows the user to feel the temperature change corresponding to deformation.”
In place of the plastic now used in PS5 DualSense controllers, this would be accomplished by utilizing a malleable elastic sensor or gel-like material. The sensor in the new PlayStation controller might alter its form to more effectively convey vibrations throughout the controller by delivering electronic impulses in response to the user’s touch. Overall, this might improve Haptic Feedback, and Sony’s patent also includes the use of artificial intelligence to detect material deformation.
There are still many problems that this new technology needs to solve, such as how the wireless controller’s battery could discharge more quickly due to the new controller’s changing temperature.
However, if this new patent makes it through the lengthy development process, it could result in a more immersive gaming experience for either the PlayStation 5 or the upcoming PlayStation 6, allowing players to better feel the shape and temperature of an in-game object through improved Haptic Feedback. The new PlayStation controller, for instance, might warm up when the player picks up a hot object or cool down to the touch to represent an icy setting.
The DualSense controller’s highly praised Haptic Feedback feature, which vibrates at different frequencies during specific gameplay moments to simulate swimming through water or driving over a rocky dirt road, is one of the many ways that the PlayStation 5 has contributed to making gaming more immersive. As a player pulls back Aloy’s bow in Horizon Forbidden West or swings Kratos’ Leviathan Ax in God of War Ragnarok, the DualSense’s triggers likewise experience a shift in resistance.
As the business continues to introduce new types of feedback to the DualSense and the new PlayStation controllers, Sony has already looked at ways to let players customize their Haptic Feedback experience and permit smaller indie games to make use of this functionality.
There is no guarantee that these concepts will ever be turned into a commercially accessible product, as with any patents, but it’s an intriguing thought nonetheless.