Since the start of the metaverse craze, many people have only had one question in mind: “What is the future of AR?”
One such cutting-edge technology that makes science fiction a reality is unquestionably augmented reality. Holograms are now all around us in the real world, just like in Star Wars and Marvel films, creating a uniquely immersive experience beyond simple entertainment. Today, augmented reality is a powerful tool for business too.
What is the future of AR?
Augmented reality is employed in a variety of different industries, including retail, commerce, gaming, healthcare, and even the military, to address a wide range of business obstacles. To understand the industry’s direction, it’s critical to keep an eye on these technologies. Now let’s answer the question you’ve had on your mind last 2 years: “What is the future of AR?”
Metaverse
You probably don’t find it surprising that augmented reality is being used in conjunction with other metaverse technologies. Since Facebook changed its name to “Meta,” the metaverse has flooded the news media. It’s not just marketing nonsense, though. Dismantling the partitions between the virtual and real worlds is one of the aims of metaverse technologies. Due to the ability of augmented reality to show virtual items that are integrated into our real world, both consumers and companies can benefit from this technology. So, “What is the future of AR?” Metaverse is the future of augmented reality.

Funny avatars
AR is a fantastic place to start if we want to integrate digital experiences into the physical world. Businesses are already developing camera filters that accomplish this using body and facial tracking, as well as sophisticated scene depth sensing. Ready Player Me and Geenee AR collaborated to make this experience a possibility. You may practically “wear” your avatar on camera by adding it to Geenee’s WebAR Builder program. Your Ready Player Me character’s cosmetic accessories, including NFT accessories, are also taken into account by the software.
It is not a new invention. You’ve seen this technology on apps like Instagram and Snapchat countless times. The app’s ability to let users import their avatar from other platforms and use it in augmented reality is its most inventive feature, though. This technique may eventually be used to hybridize online meetings. When you attend a meeting without a VR headset, but one member of your team is wearing one, they could be represented in the meeting by an AR avatar.
The biggest hurdle to entry in this field is the development of increasingly potent and affordable AR headsets. We’ll have to wait and see how technology develops.
Spatial audio
Spatial audio is crucial for boosting the immersion of AR experiences, despite the fact that it may not initially appear to be an augmented reality technology. The inclusion of all of our five senses in the process is something that metaverse technologists are preoccupied with, and this includes hearing. 3D audio is required to increase the immersion of VR and AR experiences. Based on their own position, users should be able to determine where a sound is coming from in 3D space.
Recently, Meta upgraded its AR Spark Studio with a sophisticated engine that combines various sounds to produce sound effects. This enables developers to produce multi-sensory effects that let users immerse themselves in the augmented reality experience using both sight and sound. We may respond to user interaction with our AR effect by making sounds play.

Digital experiences
Fans of the metaverse enjoy using augmented reality to bring things from the virtual to the physical world and vice versa. Actually, this technology existed long before the metaverse hype. For instance, Meta is focusing on using augmented reality to showcase digital collectibles. Creators only need to connect their NFTs with the “See in AR” functionality in Instagram Stories as 2D virtual objects. This will give artists and collectors new ways to utilize and share their NFTs outside of their wallets, and it will undoubtedly swiftly emerge as one of the most important augmented reality market trends in 2023.
There has also been some discussion over the use of real-world or virtual art in augmented-reality experiences. For instance, the fourth-oldest auction house in the world, Sotheby’s, has started providing augmented reality (AR) experiences to buyers via an Instagram filter, enabling them to view the art for the auction up close and personal. Using this technology, Sotheby’s was able to sell a painting for $121.2 million.
AR hand in hand with AI
There are two ways that artificial intelligence and augmented reality work well together:
- Software for facial and spatial recognition, which is essential for AR, is powered by artificial intelligence.
- Innovative solutions can be provided by combining AR and AI technologies.
Artificial intelligence and augmented reality are two different fields of technology. But given AR’s requirements, it’s not surprising that AI and AR get along well. Environment sensor data must be interpreted using complex algorithms. In comparison to a model created solely by humans, AI can streamline that process and increase accuracy.
The application ClipDrop is an illustration of this in action. With the help of the app, users can instantly turn a physical thing into a 3D object for usage in applications like PowerPoint, Photoshop, Google Docs, and more. Real-world objects can also be imported into metaverse settings using 3D scanning. Businesses might find that 3D scanning is a terrific method to expedite the process of offering products for virtual trial experiences.

A further application of coupling AI and AR is automatic design. An example of this technology in use is the app SketchAR. Using this software, users can doodle at will in AR. They can also employ an AI to draw for them, though. Structures can be created swiftly by AI. This demonstrates that by using the real world as the source environment, AI systems are capable of designing objects in 3D space. This may indicate that AI will eventually be able to design and produce buildings for use in the actual world.
AR in mobile technologies
Mobile devices have been one of the key platforms for distributing augmented reality experiences. The majority of customers own a mobile device, yet consumer adoption of AR headsets is still in the early stages. As a result, companies have discovered several ways to employ mobile devices for augmented reality. Over time, technology has also advanced substantially.
ARCore
Google unveiled a new geospatial experiences API in 2022. This makes it possible for developers to design experiences linked to particular virtual places. AR encounters in the past have only been relative to the user or in arbitrary places chosen by the user.
Developers can specify latitude and longitude for AR content using the geospatial API. It’s not essential to physically scan the area either. It operates very similarly to Apple ARKit Spot Anchors, comparing aerial photos of the immediate area to Google Street View photos to quickly pinpoint a precise location.

ARKit 6
At WWDC in 2022, Apple unveiled a number of new features for their ARKit 6 upgrade. One of them involves capturing a 4K video while ARKit content is being used. Scene occlusion and other experiences are now considerably more realistic thanks to an improvement to the depth API. With Apple’s LiDAR scanner, AR experiences may be created so quickly that the technique is referred to as “instant AR.”
Apple enhances its motion-capturing feature as well. When another person is in focus, motion capture data from their movements can be used for a 3D model. People occlusion, which enables virtual items to pass in front of and behind real people in the scene, is one of the other most recent improvements.
RoomPlan, a tool that uses LiDAR scanning to swiftly produce floor plans of a home or other structure, is one significant example of how these ARKit 6 features are put to use.

ARCore vs ARKit
Over the past few years, Apple and Google have mostly maintained the same level of competitiveness in the field of augmented reality. The software for both technologies is comparable to one another as normal.
Hardware is where things start to get interesting, though. The finest caliber augmented reality experiences are possible thanks to Apple’s LiDAR scanner and comparable technologies featured on more expensive Samsung handsets. But there are many different hardware variations among Android devices. Many Android smartphones are simply underpowered to support more advanced AR.
As a result, companies must plan carefully about the kinds of augmented reality experiences they wish to provide. They can use their ideas to the fullest if they want to provide high-quality experiences to a smaller, wealthy audience with the equipment that can handle them. However, a company will need to tone things down a little with a simpler app if they want to provide an accessible experience for more devices.
WebAR
WebAR is a significant augmented reality movement. WebAR doesn’t require users to download any additional software because it is powered by web browsers. The most basic AR experiences are available through WebAR, which lacks many of the features that native AR on mobile devices can provide.
WebAR, though, can occasionally be quite helpful for straightforward experiences such as changing the color of hair or items, adding filters to faces, replacing backgrounds, and creating simple 3D creations. WebAR enables more straightforward virtual try-on experiences. For their cosmetic goods, many companies, including L’Oréal and Maybelline, utilize such tools.
WebAR is the key to bridging the divide between the virtual and real worlds, according to Tom Emrich of 8th Wall, the top WebAR development platform in the world. Although WebAR isn’t very strong right now, it could become one of the most significant methods to interact with the Internet in the future. To make this vision a reality, 8th Wall is constantly enhancing WebAR technology.

Cross-platform apps
Making cross-platform apps is a significant obstacle in AR development. There is also the regrettable reality that cross-platform programs will probably fall short of native ones’ full capabilities. Cross-platform apps, however, can be of very high quality if the proper measures are taken. Cross-platform augmented reality is simpler to code and can shorten the time to market. Presentation and performance, however, can suffer.
In general, it is preferable to keep an app native if it is highly complicated and requires making use of all native features. Cross-platform will work just fine if the software is simple and doesn’t require a lot of performance, though.
Cross-platform AR is an option, for instance, if you’re building an online store with 90% of its functionality, not platform-dependent, minimal performance requirements, and a straightforward AR product preview module. However, the native alternative is preferable when dealing with applications whose functionality demands maximum performance or is platform-dependent. This is true of initiatives like 3D scanning or augmented reality navigation.
Building cross-platform applications with the greatest quality possible can be accomplished by working with an augmented reality development company. This helps you concentrate on other areas of your organization while also enabling you to increase the quality of your goods.
AR headsets
If a question like, “What is the future of AR?” is posed to us, We can simply state that AR headsets constitute at least a small part of this technology’s future. Comfortable and user-friendly AR glasses seem to be getting closer to reality with each passing year. The projected mixed reality headset for Meta, now known as Cambria, is one of the newest products that are still in development. They have a new product line that is separate from their popular Meta Quest 2.
The Cambria headset, however, appears to be targeted primarily at privileged audiences who want to get a head start on the future of augmented reality. As a result, it appears that Cambria isn’t the miracle cure that everyone had hoped for. It might be a start in the right direction, though.

The development of Apple’s LiDAR scanner is another crucial step for the future of AR. One of the main firms expected to release consumer-focused AR glasses or headsets in the future is Apple. Their cutting-edge depth sensor was installed on the iPad Pro and later iPhones.
In addition to AR glasses, there are other cutting-edge products that promise to hold a significant position among future trends in augmented reality. The first presentation of augmented reality smart contact lenses took place in June 2022 at Mojo Vision Labs in Saratoga, California. In order to provide an augmented reality experience, AR lenses connect with the user interface and rely on eye tracking, communications, and software. Mojo Lens’s specially calibrated accelerometer, gyroscope, and magnetometer continuously monitor eye movements to guarantee that AR visuals don’t move with the user’s eyes.
AR in marketing tools
In the field of marketing, augmented reality has a wide range of applications. For instance, business cards are a common and straightforward option that may be used with straightforward AR systems. You can differentiate yourself from the competition and provide potential clients with a brand-new and interesting way to learn more about your business by incorporating interactivity into marketing materials like business cards.
Businesses that want to give their consumers more thorough and feature-rich instructions and documentation frequently opt for AR manuals. In addition to enabling the engaging delivery of information, augmented reality (AR) also considerably enhances user experience without requiring the customer to expend a lot of effort to master one or more mechanisms.

There are numerous uses for AR in advertising. Users no longer find web banner adverts to be as popular as they once were. Banner ad click-through rates decreased from 0.72% in 2016 to 0.35% in 2019. One possibility for this is that the banner adverts are interfering with the user’s attempt to access the content. However, AR advertisements might offer more streamlined content access, blocking content less. For instance, users can access augmented reality experiences from their timelines using Facebook’s new augmented reality adverts, which have a variety of features. Virtual try-on, putting virtual items in their houses, and other features are a few of these.
Navigation technologies
AR navigation is easier to use and more viable than ever in 2022. Most notably, indoor navigation is now much more practical than in previous years, thanks to the development of technologies like Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) antennae, Wi-Fi RTT, and ultra-wideband (UWB). Displaying AR directions in big interior spaces like distribution centers, shopping malls, and airports is one of this technology’s most practical uses.
The capability of this technology to be used by both consumers and corporate users is something that shouldn’t be disregarded. A distribution center employee might utilize augmented reality indoor navigation to locate a specific item in their warehouse, similar to how a store visitor might. Even though glasses with AR capabilities that are comfortable and affordable aren’t quite there yet, the potential for business uses of AR in retail, distribution facilities, and other industries are there.
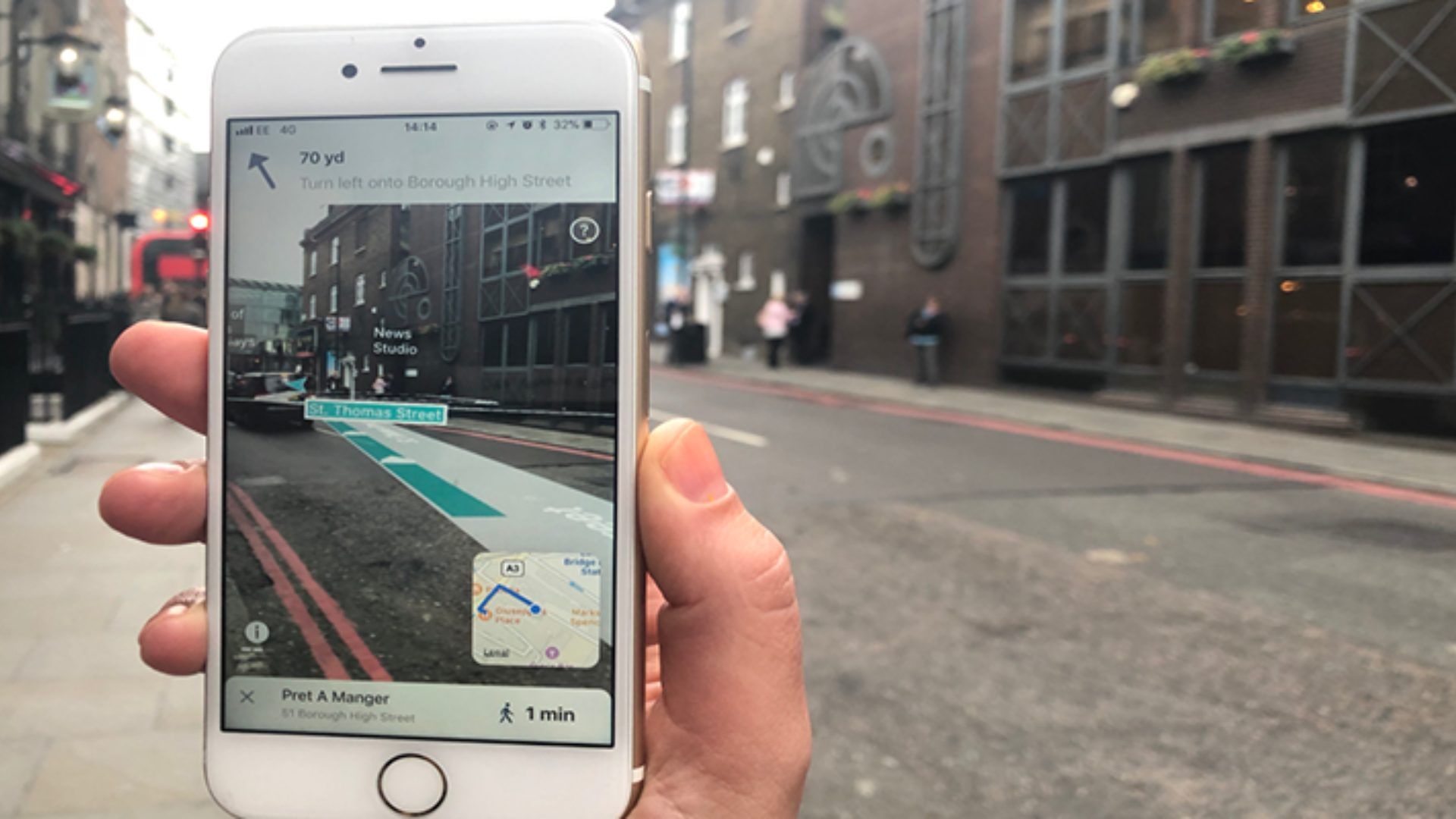

Buy online pick up in store (BOPIS) services can be made considerably more effective with the use of indoor navigation. Instead of using coordinate instructions to locate the item, team members tasked with “picking” the products in the store for order fulfillment can use augmented reality (AR) directions to navigate directly to the item. By doing this, you won’t have to waste time looking through a lot of things that are identical and locating the right aisle and department of the store. To see the instructions on the screen, all a team member needs to do is hold up their device.
However, there are some restrictions that must be considered, such as things that have gone missing throughout the store. The team members may utilize augmented reality (AR) navigation on their tablets to find an open position on a shelf if they have been moved by customers or have entered their login information mistakenly.
Creating new shopping experiences
Numerous inventions that could aid in extending experiences to online buyers were required in response to the COVID-19 outbreak. One of the technologies that benefited the most from this disruption was augmented reality. There was an explosion of online try-on options as a result.
AR technology is being actively adopted by brands to enhance the online purchasing experience. For instance, Dior has frequently introduced augmented reality (AR) shoe experiences that enable buyers to virtual test shoes before purchasing. For the first time, Dior and Snapchat collaborated to develop such a project in 2020.
Another example would be FRED. Customers can utilize a 3D configurator on the FRED Jewelry website to personalize bracelets and virtually try them on.
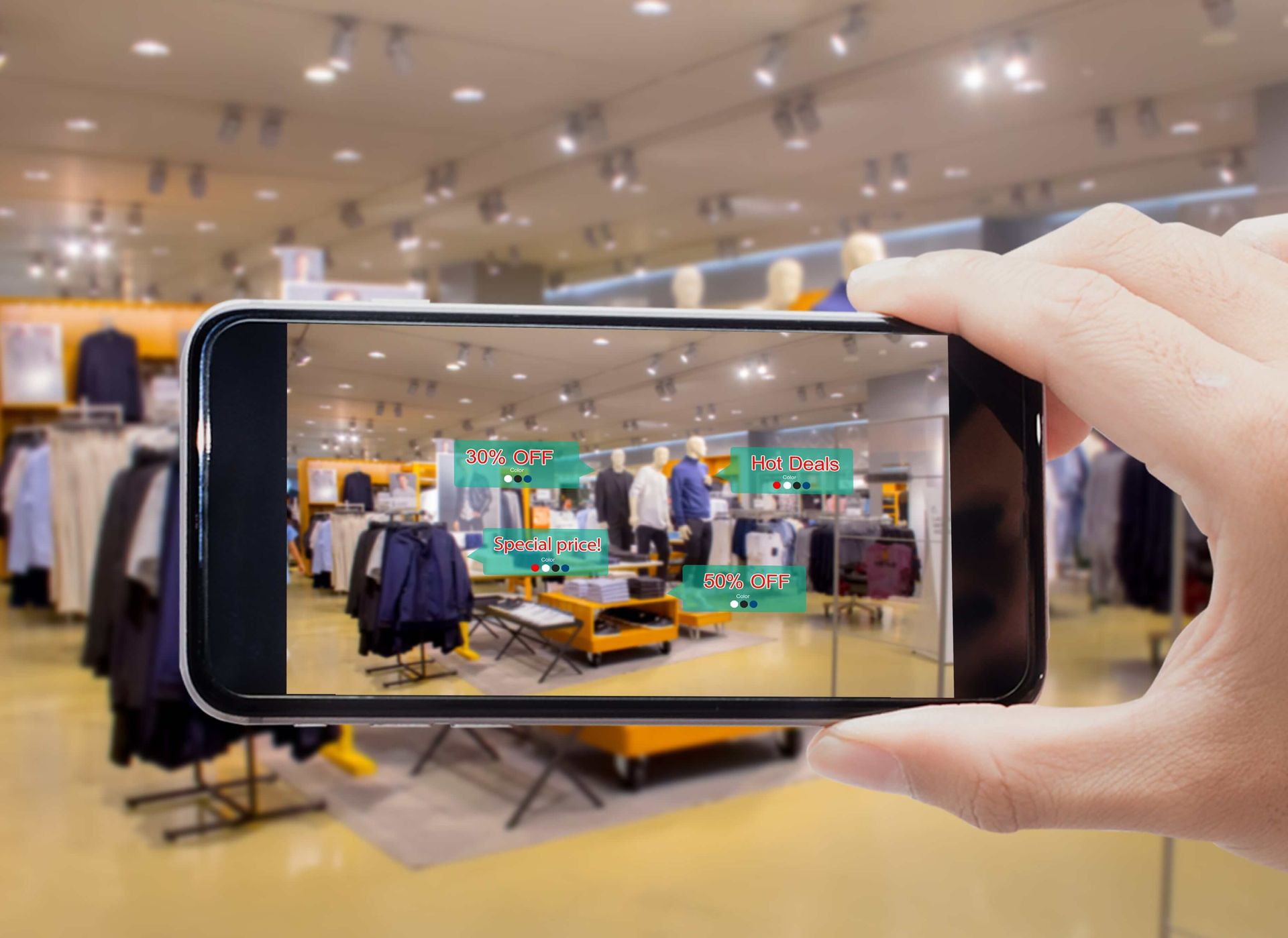

Smart mirrors
There is still room for augmented reality to improve in-store experiences once quarantine lockdowns cease and shoppers start to return to physical businesses. Smart mirrors are a fantastic method to improve the shopping experience while lightening the strain on the changing rooms. Customers can approach smart mirrors in-store and try on clothing using cutting-edge AR technologies that are not yet available on smartphones.
When clients need to have specific sizes of clothing mailed to them since they aren’t in stock in the store, smart mirrors are also useful. These requirements can be met with the use of smart mirrors and home-based virtual fitting room technology.
AR in manufacturing
A lot of AR applications are geared toward users. But there is a lot of potentials for AR to be used in sectors like manufacturing. For instance, AR experiences backed by CAD data can improve worker training. Additionally, AR can help personnel with routine maintenance procedures. To help technicians complete the task at hand, AR applications can be used to highlight certain components of the item being worked on. In general, head-mounted systems offer greater accessibility to this than smartphone apps do.
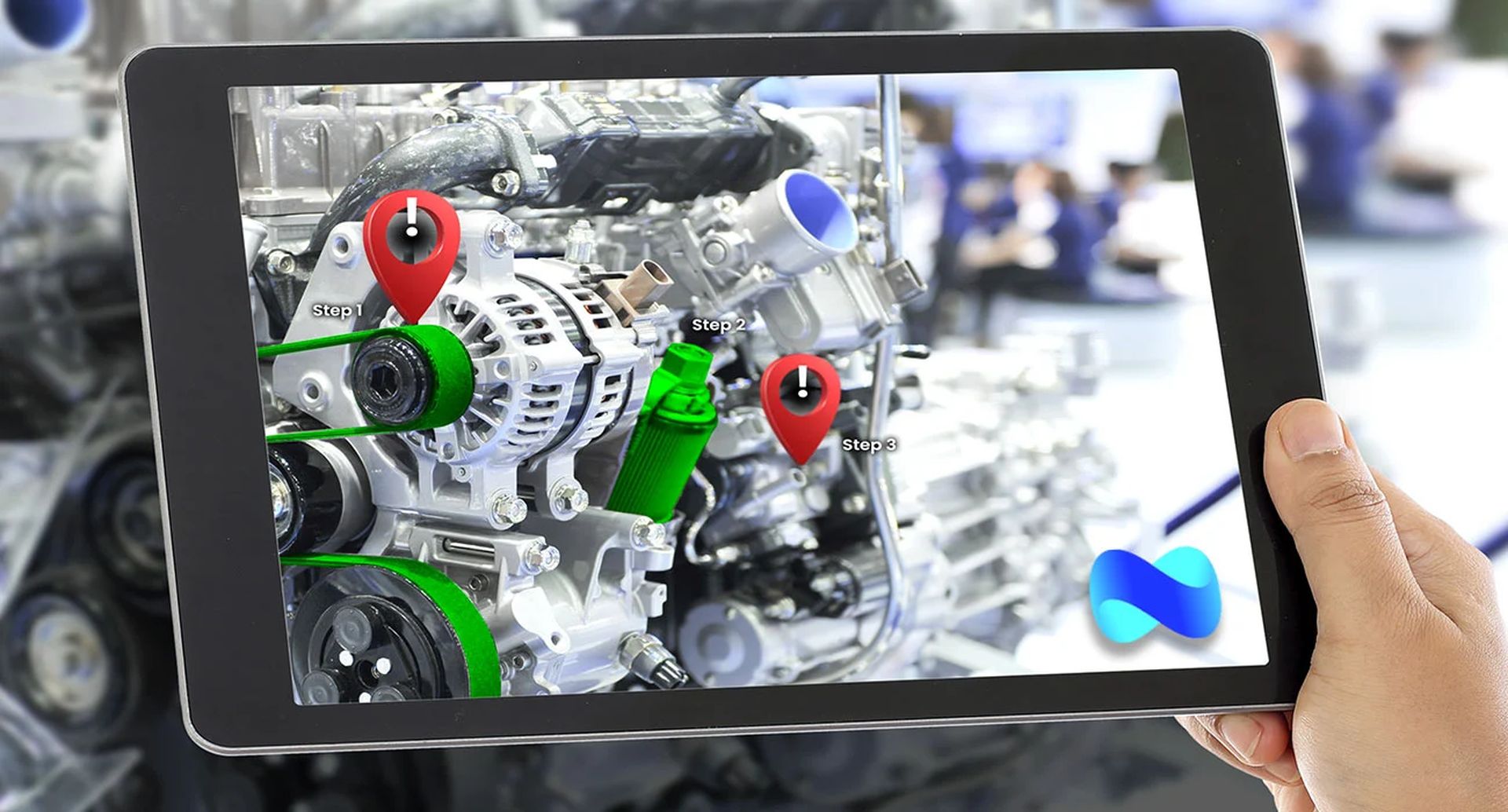
When configured properly, AR can assist provide workers with more contextual information about items in a factory in more straightforward applications. A worker can learn more about an object and determine whether any actions, such as maintenance, are required by highlighting it using a mobile device.
The promise of AR extends to remote troubleshooting as well. Workers on the other end of the conversation can follow virtual markers that remote support agents can place on the screen. As a result, factory locations may receive more thorough and beneficial remote support.
As a bonus, you can learn more about AR remote support here.
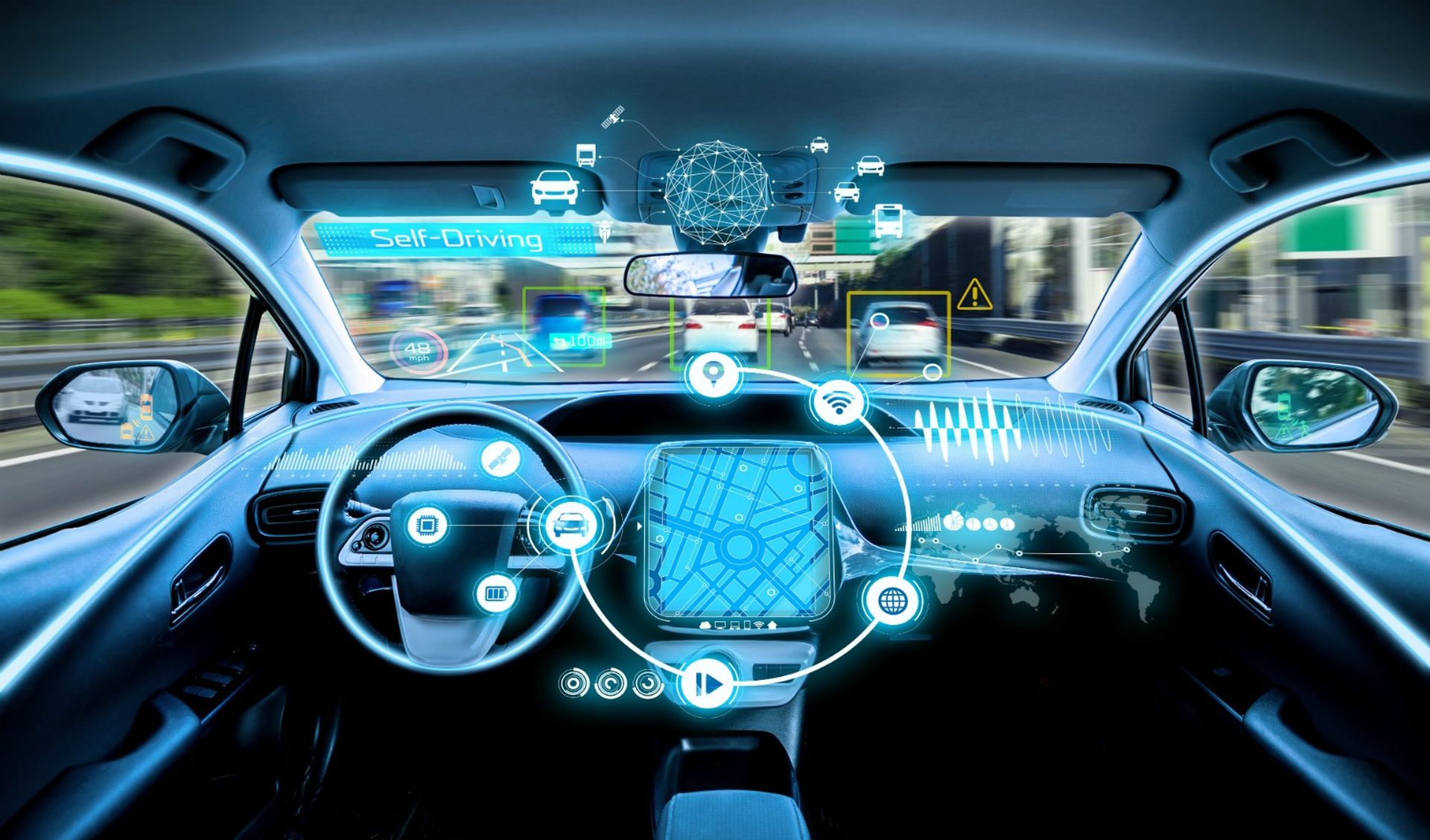
AR in cars
The automotive business may benefit from a variety of distinct augmented reality applications. One of the more intriguing and upcoming technologies in this field is augmented reality, which uses a heads-up display to highlight on-road objects (HUD). This can help keep drivers’ eyes on the road while also alerting them to risks and GPS directions. In addition to providing entertainment and information, augmented reality is used in applications like 3D automobile manuals.
Parking assistance is a fascinating utilization of augmented reality in the automotive sector. A driver’s heads-up display can be enhanced with empty parking spaces thanks to 5G connectivity. This can also offer a wealth of information that can be used to improve the designs and operations of parking facilities like lots and garages.

Conclusion
As time passes, the augmented reality business will expand, especially when customers have wider access to this technology. AR is the next stage for many firms because there has been a huge increase in the focus on metaverse technologies. Long-term investors might want to enter this market a little earlier.
Retail and mobile applications, however, might be more successful for companies trying to adapt to faster growth and change. Everywhere you look, you may find AR-capable smartphones and tablets, which offer fantastic options for advertising and extending conversion-driving user experiences.
It is obvious that augmented reality is the future for many businesses, given that the market is anticipated to reach $97.76 billion in 2028. Businesses that respond to today’s difficulties in novel and creative ways will decide that future. Businesses that provide their clients with excellent AR experiences will be considerably better able to compete with their rivals. We hope you’ve found some answers for this cliche question: “What is the future of AR?”





