The keynote of the NVIDIA GTC 2022 (GPU Technology Conference) event has concluded, and it was jam-packed with news. The new RTX 40-series (RTX 4090, RTX 4080) graphics cards, which marked the beginning of a completely new generation of graphics cards for PC gamers, were undoubtedly the most notable announcements.
But as usual, NVIDIA‘s statement included a wide range of topics beyond consumer gaming, including innovations in the robotics and self-driving vehicle industries as well as advances in research and medical.
GeForce RTX 4090 and 4080
Three new graphics cards were of course the main news that began the speech. The flagship model is the RTX 4090, which according to NVIDIA is up to 2 times quicker than the RTX 3090 Ti in rasterized games. This enormous card is based on Ada Lovelace, who served as the inspiration for all of the GTC announcements. It has 24GB of GDDR6X memory and 16,384 CUDA cores. Most significantly, it has 450 watts of power, the same as the RTX 3090 Ti.
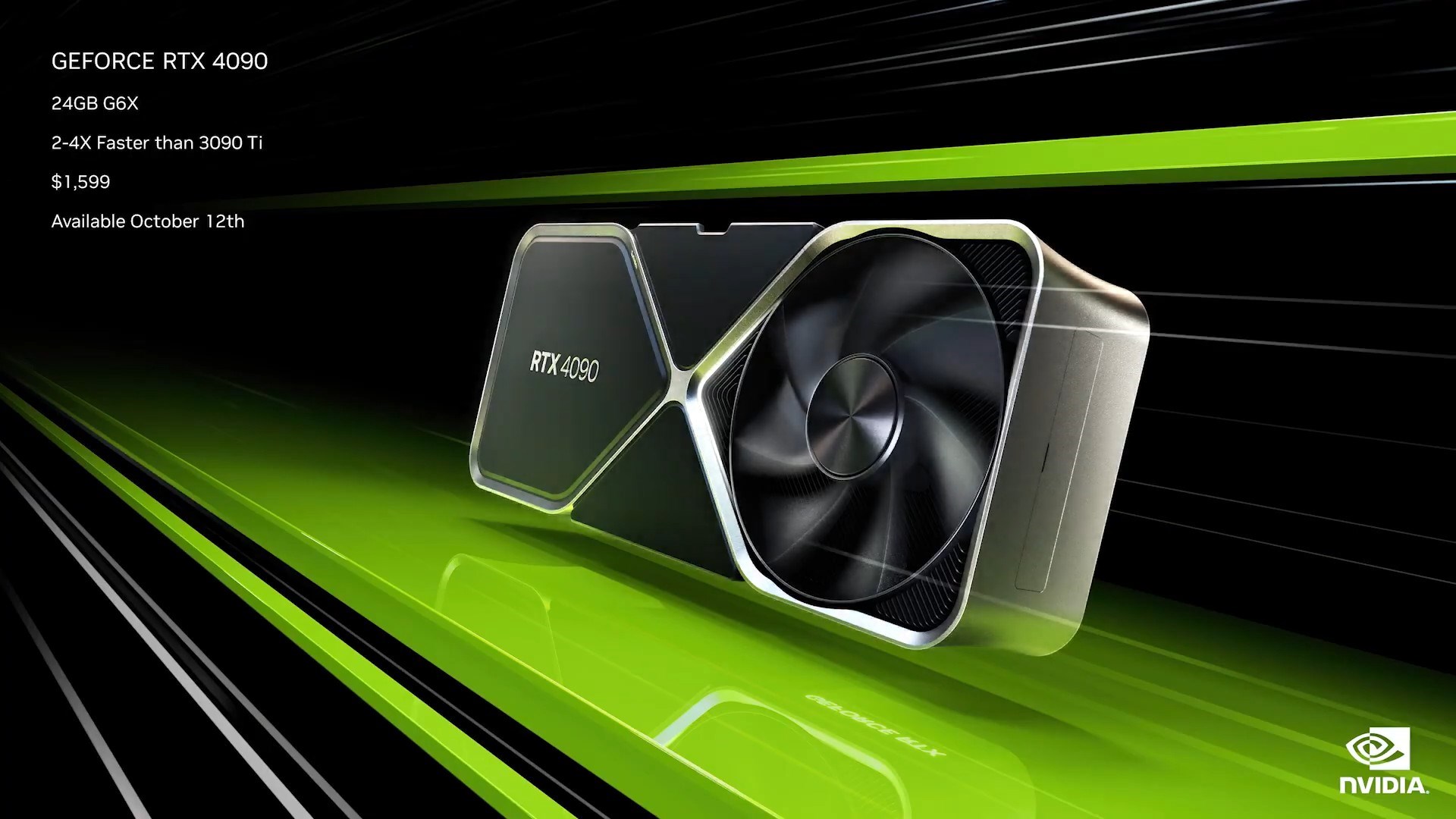

The RTX 4090 will cost $1,599 and be obtainable on October 12.
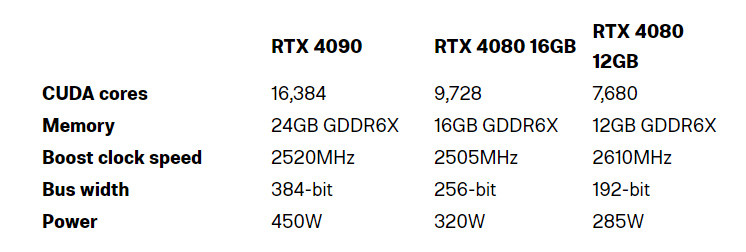
From there, the RTX 4080 is a step down and is offered in two different configurations. The price for the 16GB variant is $1,199, while the price for the 12GB model is $900.

These GPUs have 320w or 285w, which is a little bit more tolerable. However, there is a significant difference in the CUDA core count of the RTX 4090 and the RTX 4090 12GB variant. It would be fascinating to see how these two RTX 4080 models compare in terms of performance given the significant differences in their specifications.

NVIDIA also unveiled the third generation of RTX, which incorporates DLSS 3, along with the new GPUs. This seems to be a significant progression of the technique, similar to moving from DLSS to the second generation. Games’ frame rates will increase much more now that machine learning can forecast actual frames rather than simply pixels.
How soon? NVIDIA claims that the optical flow accelerator can make processing up to four times faster. Actually, this technology combines three distinct NVIDIA innovations—DLSS Super Resolution, DLSS Frame Generation, and NVIDIA Reflex—into one.
NVIDIA DLSS 3
The capacity of DLSS 3 to improve CPU-restricted games is its second major feature. Microsoft Flight Simulator, which is a program that perfectly fits the bill, was demonstrated by NVIDIA. It’s quite astonishing to see DLSS 3 increase frame rates from 64 fps to 135 fps, especially in this kind of game. Overall, NVIDIA claims that DLSS 3 will be four times faster than traditional rendering. NVIDIA claims that more than 35 games and programs will support DLSS 3 when it launches in October. Last but not least, NVIDIA unveiled Portal RTX, an updated version of the well-known PC game that has DLSS 3 and ray tracing effects.
NVIDIA Drive Thor
NVIDIA has been working for years to establish a foothold in the self-driving vehicle industry, but its most recent product feels like a big move in the right way. Its newest superchip, NVIDIA Drive Thor, is built on the Hopper GPU architecture and is combined with the NVIDIA Grace CPU.
Drive The inference transformer engine originally appeared in an automobile platform called Thor.
Drive Thor, which NVIDIA claims will be the actual replacement for Drive Orin, which is presently in production, will be offered for automakers’ 2025 vehicle models. Drive Atlan, which had only recently been unveiled, is replaced by Thor.
NVIDIA Drive Concierge
NVIDIA demonstrated Drive Concierge, a comprehensive in-car infotainment system, together with the new processor. With what NVIDIA refers to as a “digital cockpit,” the instrument cluster on a normal car dashboard is replaced. The technology is compatible with Android Automotive, which enables automakers to personalize systems. Notably, the announcement comes only a few months after Apple’s historic unveiling of next-generation CarPlay, which uses its digital instrument cluster in a similar way.
Of course, Drive Concierge also offers passengers services elsewhere in the car, including as video conferencing, streaming, digital assistants, cloud gaming with GeForce Now, and complete visualizations of the vehicle. NVIDIA claims that creating in Omniverse enables automakers to change all these components of the car long before they become a physical reality. The entire design was produced in this manner.
Omniverse Cloud and NVIDIA’s Graphics Delivery Network
NVIDIA’s whole package of cloud services, Omniverse Cloud, was introduced earlier this year to help people build the metaverse of the future without having to use their own computers to handle all that processing power. The robotics simulation program NVIDIA Isaac Sim and the simulation for autonomous vehicles NVIDIA Drive Sim are recent additions to the package of offerings.
It’s interesting to note that the distributed data center that powers Omniverse Cloud, the NVIDIA Graphics Delivery Network (GDN), was also addressed. The GDN is the network that provides all of these high-performance, low latency graphics to anyone who needs them. It is built on the same characteristics as GeForce Now, the company’s cloud gaming service.
NVIDIA spoke extensively about the applications for Omniverse and digital twins, even asserting that any product in the future that is controlled by software will need a digital twin for testing.
Jetson Orin Nano
The newest member of the Jetson series of portable computers designed for boosting robotics and AI processes was just revealed by NVIDIA. The performance of these new “system-on-modules” is said to be up to 40 trillion operations per second (TOPS), which is 80 times that of its forerunner, the Orin NX modules.
Beginning in January, the 8GB model of the Orin Nano modules will be priced at $199.
Other introductions:
- The NeMo API for applications in natural language AI and BioNeMo for applications in chemistry and biology are two new huge language models that Nvidia has introduced.
- According to Lowe’s announcement, other Omniverse creators will be able to use its collection of more than 600 photorealistic 3D product models without charge. The business also talked about its investigation into employing Magic Leap 2 AR headsets and interactive digital twins to grant staff “superpowers.”
- The Omniverse is being used by the Deutsche Bahn Rail Network in Germany to construct the future rail network utilizing digital twins.
- The L40 GPU-powered second iteration of NVIDIA OVX, designed for creating “complex industrial digital twins,” has been introduced. For these demanding Omniverse workloads, L40 uses third-generation RT cores and fourth-generation Tensor cores, and it has already been supplied to businesses like BMW and Jaguar Land Rover. By the beginning of 2023, these new OVX systems will be offered by Lenovo, Inspur, and Supermicro.
- According to an announcement from NVIDIA, the H100 Tensor Core GPU is now in full production and will launch its first Hopper-based products in October.
- In the field of medicine, NVIDIA has introduced IGX, a platform that combines hardware and software and is intended for use cases including robotic-assisted surgeries and patient monitoring.
- NVIDIA also showed how IGX has uses in the industrial sector, particularly in the development of secure autonomous factories that entail human-machine cooperation.
- A collaboration between NVIDIA and The Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard introduces GPU-accelerated Clara Parabricks software to the Terra biomedical data platform, enabling researchers to 24x faster do activities like genome sequencing. According to NVIDIA, it would “assist discover genetic variations that are connected with diseases” by supplying its own deep learning model.
- Based on NVIDIA’s Morpheus framework, NVIDIA and Booz Allen have announced a “extended collaboration” to employ AI through GPU acceleration of its cybersecurity platform.
Do you know Gaming Istanbul breaks the most female attendees record.





