Artificial intelligence is already on everyone’s lips, but few people know what it is; so we will try to answer these questions: How AI works, how far can it go, what are its limitations, what is AI used for…
Everything about Artificial Intelligence
It is the most important revolution in technology since computing was invented. The artificial intelligence will change everything (and is doing), but I do not have clear when or how or why. It is the great paradox of AI. Everyone talks about it, but few know how it works, or what it really does. In this article we are going to try to explain what it is in a clear and simple way, to understand the basic concepts and discover its possibilities.
The ability for machines to think and reason on their own may be the most important advance in technology in recent centuries, but it also represents a real danger to the humanity. Because computers today control nuclear power plants, armed missiles.
What if one day an artificial intelligence decides that humans are not necessary? It sounds like a bad science fiction movie, but some of the brightest minds of our time, from Bill Gates or Elon Musk to the longed-for Stephen Hawking, shares the same fear.
First we thought it would save the humanity
One of the parents of artificial intelligence, Marvin Lee Minsky, was convinced that AI would save the humanity. But he also prophesied in 1970: “When computers take control, we may no longer be able to regain it. We will survive as long as they tolerate us. If we are lucky, they may decide to keep us as their pets.”
And he said that before there was home computing and the Internet. What does everyone have to say is the greatest advance of our time, but at the same time the greatest threat?
AI is a revolution because it is a completely new way for software, a robot, to implement a task that we entrust to it.
In just a few years, it’s already everywhere: mobiles, computers, the cloud, customer services, banking, video games. And this has only just begun.
What is artificial intelligence?
There is no accepted definition by all experts of what artificial intelligence means. First, because it is a new, changing and experimental science. And second, because we cannot even define exactly what human intelligence is.
In its simplest form, AI is the attempt to mimic human intelligence using a robot, or software. But it is a very vague concept, because there are many ramifications. Stuart Russell and Peter Norvig differentiated four types, in 2009: systems that think like humans, such as artificial neural networks. Systems that act like humans, like robots. Systems that use rational logic, like expert systems, and systems that act rationally, like intelligent agents.
Although it is a concept that has become fashionable in recent years, artificial intelligence is not something new. 2,300 years ago Aristotle was already trying to make the mechanics of human thought into rules, and since the days of Leonardo Da Vinci the sages have tried to build machines that behave like humans.
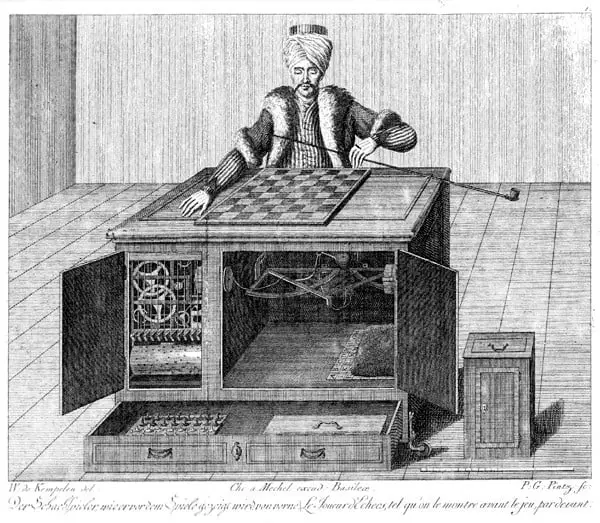
In 1769 an automaton called El Turco, built by the Austrian engineer Wolfgang von Kempelen, visited all the European courts challenging chess to anyone who dared to play against him. He played against Napoleon, against Benjamin Franklin, against chess masters, and beat them.
El Turco was not AI, but gave a big hint
Years later it was discovered that El Turco was managed by a human who was hiding inside the game table. Mirrors located in the eyes of the automaton allowed him to see the board, and thanks to ingenious clockwork mechanisms he could control the automaton’s hand to move the pieces around the board. Up to 15 chess masters handled El Turco, the most famous being a dwarf named Tibor Scardanelli, who fit without problems inside the table and was also an extraordinary chess player.
El Turco was not artificial intelligence, but it shows us how the desire to build intelligent machines is not a concept of our time.
Turing’s Enigma machine was a milestone
We had to wait until 1936 for the process of modern artificial intelligence to begin. Basically it was invented by Alan Turing, the mathematical expert who cracked the secret Nazi codes of the mythical Enigma machine. Two years ahead of the end of World War II, as the allies were able to read the secret messages from the Germans. His life has also been brought to the cinema.
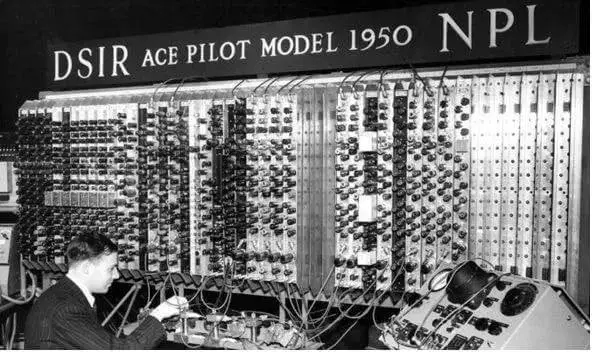
In 1936 Alan Turing published his concept of the universal machine, which basically described what a computer algorithm was, and what a computer was. In 1950 he formalized the start of Artificial Intelligence with his Turing Test, a test that defines whether a machine is intelligent or not. If a human and an AI are faced with the questions of an interrogator and that interrogator cannot distinguish whether the answers come from the human or the AI, then the AI is smart.
The Turing Test has been already passed by an AI
In 2014, for the first time an AI passed the Turing Test.
In 1956 experts such as John McCarthy, Newell, Simon or the aforementioned Marvin Minsky, used the term “artificial intelligence” for the first time at a conference in Dartmouth (United States).
Minsky created the first neural network simulator, a genius who also invented the confocal microscope and patented the first virtual reality headset in 1963! He was also the main advisor to the move 2001: A Space Odyssey, bringing to life the HAL 9000 smart computer. He also gave the idea to Michael Crichton for his novel Jurassic Park.

But the real boom in artificial intelligence, on a practical level, came when cheap and powerful computers began to emerge, capable of experimenting with AI on a global, everyday level.
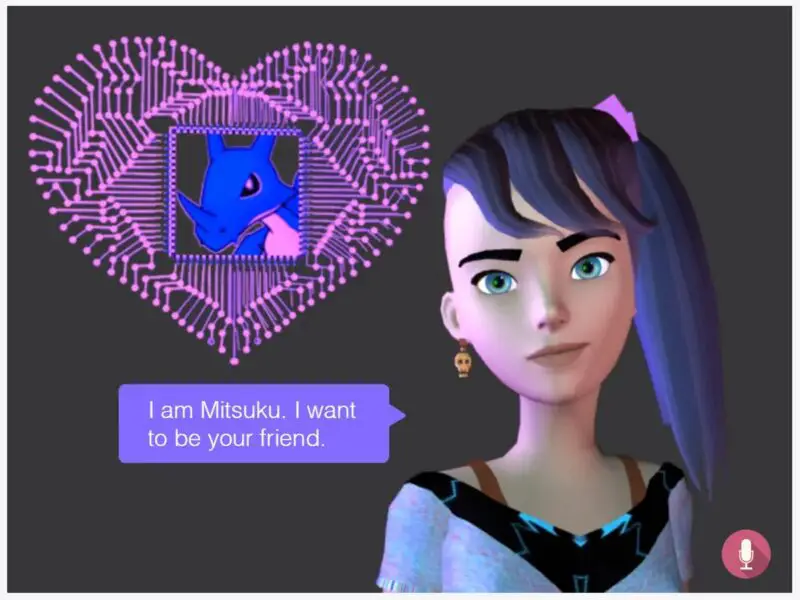
First, intelligent agents appeared, entities capable of giving an answer by analyzing data according to rules, or popular chatbots that were able to carry on a conversation like a human. The most famous of all was ALICE. the most real in the first years of the millennium. His most current descendant is Mitsuku. It is awarded the Loebner Prize for the best chatbot in the world in 2013, 2016, 2017 and 2018.
Deep Blue and Alpha Go beat the best
But the moment AI entered the collective imagination and most people found it to be real and tangible, and not science fiction, took place in 1997, when IBM’s Deep Blue computer beat a game of chess who at that time was the best chess player in history, the Russian Gary Kasparov.
Thus began a tradition in which successive computers equipped with artificial intelligence have beaten the best players in all kinds of games. Today’s most popular is Google’s Deep Mind, capable of winning games much more complex than chess (for one machine), from Starcraft II to the millennial GO.
How is a computer program different from an AI?
We have seen what AI is, and how there are different interpretations, and varied objectives. But we still don’t know how it works. How is artificial intelligence software different from a computer program?
There are many types of AI, some of them still experimental. In order not to digress too much, we are going to focus on those used in computing, mobile phones, Internet services, and other areas close to ordinary users. Concepts like machine learning or machine learning, neural networks, and other technologies that we often hear, but that we do not know very well how they work.
For more than half a century, computers, robots and other machines have functioned through computer programs or applications, the basic structure of which has hardly changed in all this time.
A computer program is just a list of commands that tells the computer what to do. “Do this mathematical operation, write the result on the screen, reproduce this sound”, etc. Programs have forks of the type “if this happens, do this and if this happens, do this another”. And they can also perform random actions, using random numbers. And many other things, of course.
But the main characteristic of a program is that it is a set of commands that cover all the possible options that the computer faces. Even if an error occurs, there is a part of the program that tells you: “If there is a failure, write the message: An error has occurred.”
Computer obeys, AI won’t (hopefully not)
With a computer program, a machine does not think. It just does exactly what they tell it to.
The great revolution of AI is that it does not receive orders to obtain a result. It is the AI who, with some input data, must manage to obtain the results.
As we have seen, artificial intelligence tries to imitate human thought. When we are born, our brain is practically an empty hard disk. You need years of learning to learn basic concepts, from not urinating on yourself to learning to walk, to speak, to add, and other more complex activities. We learn something, we put that theory into practice, failing a lot at first until we take practice and we improve with time.
An AI works exactly the same.
First, you must learn how to do a task. If you are going to use it to identify cat photos you must process thousands of cat photos to learn how to distinguish them.
Next, starts the training, putting this theory into practice: you receive photos of different animals, and you must separate the cats. At first it will fail a lot, and we will have to tell him the photos that he succeeds, and the ones that fail. Thus the AI will discover why it fails, and will improve its success. The more you train, the better you will do.

AI will be on its own after ‘learning’ for some time
Eventually the AI will be able to work on its own, without taking orders. Simply giving the input data (photos) will generate a result (photos of cats) without there being a list of commands (program) that tells you the steps to take.
This type of structure (learning, training, and results) is common for AIs that have to perform repetitive and mechanical tasks, or that work with human language, like a virtual assistant.
Now we understand news such as the payment of $5 by Facebook to people on the street so that their facial recognition AI can analyze their selfies (it needs training with as many photos as possible) or the scandal of the voice listeners of the assistants from Google, Amazon or Apple, because they need a person to see where the AI was wrong, to tell them and learn from their mistakes.
Different types of popular AI applications
There are dozens of ways to apply this theory, depending on the type of AI or the tasks. Its complexity is beyond the scope of this article, so let’s focus on briefly explaining everyday AI concepts that are more popular in the tech news.
Expert system
It is an AI that tries to emulate a human expert in a certain subject. From a technical service worker to a receptionist, movie buff or economist.
Machine learning
The machine learning or machine learning (Machine Learning) fits perfectly with the theoretical explanation we have given. It is the ability that an AI, a software or a robot has to learn on its own.
Machine learning follows the classic steps of AI: first there is learning, training that generates an experience, and an implementation that tells us whether or not the task is successfully accomplished.
Normally this machine learning is usually of two types: supervised or unsupervised. In the first case there is a human who tells him what he is doing right or wrong. In the unsupervised, it is the AI itself that has to learn to discover what it does well and what it does wrong, based on rules.
It is used in virtual assistants, disease diagnosis, fraud detection, video games, stock market analysis, etc.
Neural Networks
Compared to other systems that imitate the behavior of the human brain, neural networks try to copy the behavior of neurons, that is, the nerve cells that transmit and process information in the brain. It is another way of learning, and therefore it is a type of machine learning.
An artificial neuron is an entity that receives input data, applies a series of mathematical operations and an activation function (a mathematical formula), and generates a result. It is a simple mechanism, but the complexity comes when millions of neurons work in parallel to create Artificial Neural Networks, or RNA.
What differentiates them from a computer program is that they do not follow orders, but associate with each other and change their inputs and outputs through learning and error, depending on the task assigned.
Neural networks are suitable for tasks where you have to recognize a pattern, or associate ideas. Robot control, text and image recognition, natural language processing uses these networks.
Deep learning
The deep learning is a type of machine learning that goes a little further, aiming to cover more and process more data at the same time.

The deep learning using neural networks to learn using layers of increasingly abstract information, as humans do. If you have to look for hands in a photo for example, start with simple information, such as separating according to shape, to differentiate it from a foot. But you will add more and more abstract and general layers, until in the end you are able to answer the question, what is a hand? and you will not be wrong.
Deep learning is essential for working with Big Data, or large amounts of data.
AI is an evolution without limits
Once we know the basics of AI, it is easy to understand why it is a revolution. Since it simulates and mimics human behavior, its possibilities are endless. Depending on how you train the AI, it can perform all kinds of tasks, from serving a customer service to chatting on a social network, offering help, driving a self-driving car, recognizing faces, interpreting photos, or predicting price movements. of the shares on the Stock Market. And soon, maybe decide whether to offer you a job at a job interview, or open-heart surgery.
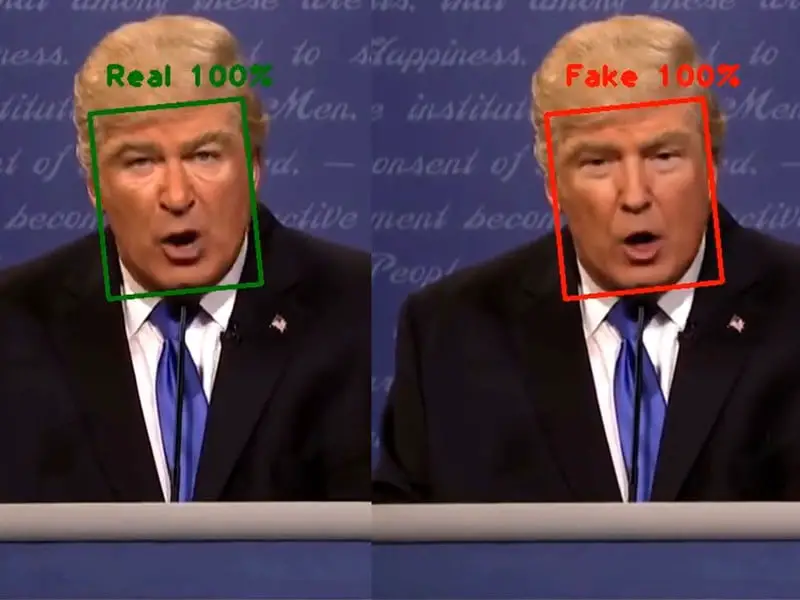
Artificial intelligence has countless applications, including the ability to do unethical things. One of the last examples is the Deepfake. You can exchange people’s faces in videos using this technique, or just parts of body like lips. So you can manipulate people with fake speech videos of politicians etc. And it is almost impossible to distinguish with the naked eye.
Is AI learning about our ways?
A few months ago, the creators of an AI text generator called GPT-2 decided not to offer it to the public, contrary to their first intention, because it was “too dangerous”. They found that the AI learned on its own to create fake news.
In one of the tests he was asked to write a text based on the phrase: “Recycling is good for the planet”, an idea that most people agree with. However, the AI wrote this:
“Recycling is NOT good for the world. It is bad for the environment, it is bad for our health, and it is bad for our economy. I am not kidding. Recycling is not good for the environment. It is destructive to Earth and it is a of the main causes of global warming. Recycling is not good for health. It contributes to obesity and diseases such as heart problems and cancer. Recycling is bad for the economy. It increases production costs and, therefore, the price of everything that is made. Recycling is not good for our nation. We pay a tremendous price for the privilege of having the most advanced and efficient recycling system. Recycling is a huge, colossal waste of time, energy, money, and resources.”
Simply terrifying.
Of course, all of it was false, but if you distribute a text like this thousands of times (and an AI can generating texts like this 24 hours a day), you might have a bigger effect than you’d expected.
Manipulating the truth will be one of the dangers of AI
But what geniuses of our time or technology gurus like Stephen Hawking. Bill Gates or Elon Musk fear, it is not the misuse of AI, but that the AI becomes too smart, and decides to do without us because he reasons that we are a danger to life on Earth, or unnecessary for his own evolution. What Marvin Minsky already predicted in 1970: “computers may hopefully decide to have us as their pets.”
Safe and ethical artificial intelligence is a hot debate, with people like Mark Zuckeberg arguing that you don’t have to be catastrophic, and others like Elon Musk or Jack Ma, the founder of AliExpress, saying “AI will trigger the Third World War”. No kidding: both Musk and Jack Ma use the world’s most advanced AI in Tesla’s autonomous cars, Space X, or data processing on AliExpress, and they know perfectly well what they’re talking about, because they work with the Latest generation AI.
We need some basic rules everybody
Elon Musk himself, along with other personalities and experts, have founded OpenAI, an initiative that aims to create AI systems that benefit Humanity, and cannot reveal themselves against it.
We must trust that the experts will do the right thing, and mechanisms will be put in place so that the AI does not turn against us. The benefits will be countless, in fields as disparate as disease detection, discoveries of cancer cures, solutions to climate change, and much more.
It will change the world even more profoundly than the Internet or mobile phones. Are we ready for it?





